2. 广东省土地利用与整治重点实验室, 广州 510642;
3. 广东省土地信息工程技术研究中心, 广州 510642;
4. 湖南省国土资源规划院, 长沙 410007;
5. 湖南省第二测绘院, 长沙 410119
2. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Land Use and Consolidation, Guangzhou 510642, China;
3. Guangdong Province Engineering Research Center for Land Information Technology, Guangzhou 510642, China;
4. Hunan Land and Resources Planning Institute, Changsha 410007, China;
5. Hunan Second Surveying and Mapping Institute, Changsha 410119, China
耕地资源是农民最基本的生产资料与生活保障,党的十九大报告中,习近平总书记明确指出“耕地是粮食生产的命根子,必须站在历史和全局的高度,坚持实行最严格的耕地保护制度,坚决守住耕地保护红线和粮食安全底线”。在目前快速城市化进程中,耕地资源大量流失,中国城市化水平从1978年的17.92%上升到2018年的59.15%[1],2030年将上升至70%[2],逐年上升的城镇化率与工业化率使我国耕地资源不断被占用,已逼近18亿亩(1亩=667 m2)耕地红线。尽管我国出台了耕地占补平衡政策,但耕地质量却因补充的低质量耕地而呈现下降的趋势;此外,现代农业中化肥、农药的过量施用导致耕地土壤质量下降,加剧了耕地资源质量的恶化[3-4]。飞速的经济发展与城市化进程之下,耕地撂荒不断涌现、优质耕地减少、耕地污染等已经威胁到耕地粮食生产能力与耕地利用保护。
耕地资源承载力是对区域耕地、粮食、人口与社会发展的系统透视,是制定区域发展战略和长期规划的重要依据[5]。早期的研究中将耕地资源承载力定义为一定时期、一定生活水准下某一地区能够供养的人口限度[6],随后,胡新艳等[7]将粮食产量纳入概念范围之中。在土地利用现状分类标准中,耕地作为第一大类,与土地的联系十分密切,因此,耕地资源承载力与土地资源承载力的发展和演变是分不开的。目前耕地资源承载力以及土地资源承载力的研究,基本上都以粮食生产与人口数量为主线,关注粮食产能与人口容量之间的关系等。因而,研究耕地资源承载力可以掌握耕地、粮食和人口之间的关系,制定合理耕地资源保护政策和耕地质量提升措施,科学地确定保护粮食安全的产能规模与基线,同时有助于预测和控制人口发展规模。
然而,研究和讨论耕地资源承载力时,因其具有时间性、空间限制性、开放性等属性[8-9],所以耕地资源承载力研究通常会涉及到复杂的自然、经济、社会要素,并受到这三方面影响因素的驱动。目前的研究虽普遍将这些影响因素指标化,通过定性或定量的方法,使其能够运用到耕地资源承载力的计算和评价中,但仍然缺乏科学有效的影响因素识别方法,导致影响因素的选取或识别具有较大的不确定性和主观性[10-11]。因此,本文对承载力的概念以及土地和耕地资源承载力评价的主要模型、影响因素识别方法进行了回顾,梳理比较了各类模型和方法的优缺点。最后聚焦于耕地资源承载力领域,针对目前耕地资源承载力评价方法中存在的问题提出了相关建议,展望了耕地资源承载力研究对保障粮食安全、助力乡村振兴方面的作用与意义。
1 耕地承载力研究现状 1.1 承载力的概念与发展承载力最初源自工程地质领域,其本意是指地基的强度对建筑物负重的能力,是评价地基稳定性的参数[12]。1798年,英国人口学家Malthus发表了著名的《人口原理》一书,提出地球能容纳的人口数量是有限的,是承载力概念在人口问题上最初的体现和应用。Verhlust[13]根据该观点建立了logistic方程,使承载力的概念有了具体的表达式和数学内涵[14]。1921年,Park等[15]在有关研究中将承载力概念扩展至生态学领域,将承载力表述为某一特定环境条件下(主要指生存空间、营养物质、阳光等生态因子的组合),某种个体存在数量的最高极限。而后,Odum[16]在《生态学基本原理》一书中将承载力定义为在某种环境条件下,某种生物个体可存活的最大数量的潜力。由上可知,承载力概念萌芽于生态学与生物学的认识,这时期的承载力特点是关注极限的容纳量,并没有涉及到对承载力运作机制的研究,研究对象的范畴也十分有限。至20世纪末,随着自然资源消耗和环境恶化等全球性问题的爆发,承载力的概念被逐步引用到资源环境领域的研究中[17-20]。引用过程中,承载力概念的发展经历了种群承载力(研究极限容纳量)、资源承载力(研究单要素的自然资源)、环境承载力(研究生态环境)和生态承载力(研究区域综合资源环境)四个阶段[21-30]。
总之,承载力并非一个静态的、固定不变的极限承载数量,而是取决于技术手段、资源偏好以及生产消费结构的非线性的动态概念[22]。在应用层面上,承载力融入了生态学和生物学、人口生态学等研究领域[31],在实践层面上,承载力可表现为一定时期一定技术水平下特定自然资源对人口或经济发展的承载能力(资源承载力),或某一区域环境对人类社会经济活动的承载容量(环境承载力)等。因此,承载力的概念逐步由单一系统要素的相互作用关系发展成具有整体性、动态性和复杂系统特征的复合概念。
1.2 耕地资源承载力研究现状第二次工业革命之后,自然资源的可持续利用问题促使学者们愈来愈关注单要素的资源承载力研究[32-34],如水资源承载力、土地资源承载力和耕地资源承载力等。土地作为人类赖以生存的自然资源之一,土地能够生产多少粮食、能够承载多少人口等有关土地资源承载力的研究成为自然资源领域关注的焦点。
而耕地资源承载力与土地资源承载力有着十分紧密的联系。20世纪80年代至20世纪末,土地资源承载力的绝大部分研究只将耕地资源作为代表性的土地资源进行研究,而并没有拓展到整个土地资源领域[35-37],直至21世纪初,才逐渐开始拓展到城市土地资源领域[38-40]。本文旨在对土地资源承载力、耕地资源承载力的研究现状进行总结,并以此为基础对关键影响因素识别以及耕地资源承载力评价模型的发展进程进行讨论。
1.2.1 土地资源承载力土地资源作为人类生存所需的重要自然资源,自Park等[15]在1921年首次在生态学领域提出承载力的概念之后,土地资源承载力就成为了承载力研究中开始较早且研究历史最长、研究成果最多、最为成熟和完善的领域。土地资源承载力通常与人口数量、粮食产能相联系,1965年,Allan[41]提出了以粮食为标准的土地资源承载力计算公式,但公式中缺乏对资源要素和人类活动之间相互作用的考虑,比较片面,属于一种粗略的计算。1970—1980年,澳大利亚学者以及联合国粮农组织分别采用了多目标决策分析法和AEZ法(农业生态区法)对澳大利亚及发展中国家的土地资源承载力进行了计算[42-44]。20世纪80年代初,英国科学家基于系统动力学方法,提出了一种新的土地资源承载力计算模型(ECCO模型),用于模拟区域人口数量与承载力之间的关系。
中国的土地资源承载力研究正式起步的标志是1986年由中国科学院自然资源综合考察委员会主持的“中国土地资源生产能力及人口承载量研究”项目的完成。该项目为中国的土地资源承载力研究开辟了道路,而1989—2000年期间完成的“中国土地的食物生产潜力和人口承载潜力研究”与“中国农业资源综合生产能力与人口承载能力研究”更是进一步奠定了中国土地资源承载力研究的理论基础[45-47]。但目前土地资源承载力的概念并未统一,其中具有代表性的定义由封志明等[36]提出,认为土地资源承载力一般是指一定地区的土地所能持续供养的人口数量,即土地资源人口承载量,其实质是研究人口消费与食物生产、人类需求与资源供给间的平衡关系问题。
进入21世纪,随着信息技术、硬件设备等各领域研究的创新和进步,加之新时代国家对于乡村振兴、生态文明建设等方面的重视,许多学者对土地资源承载力的研究领域和评价方法进行了拓展和创新。有学者借助ArcGIS等计算机软件,运用相关评价模型,对土地资源承载力进行评价[48-51];还有一部分学者通过构建土地资源承载力影响因素评价指标体系,从自然要素、社会经济要素对承载力限制的角度,进行综合的土地资源承载力评价[39, 52-53]。
从近年来的研究中可以看出,土地资源承载力仍以粮食产能、人口承载为核心内容,但研究重心已从结果计算向研究过程与机理转移[54],土地资源承载力系统中各要素之间相互作用机制的分析将成为将来研究的重要发展方向。
1.2.2 耕地资源承载力耕地资源承载力是土地资源承载力的进一步深入和细化。耕地作为土地类型的一种,具有与土地高度重合的自然、社会属性,并且人类对土地资源承载力的关注与研究已有近400年的历史[55],所以土地资源承载力为耕地资源承载力提供了坚实的理论研究基础以及方法上的参考。耕地资源承载力研究的实践基础来自于我国改革开放以来为提升耕地质量所做的各项调查研究[56-57]。如土地资源调查、农用地分等定级估价、农用地产能核算、耕地质量调查与监测、耕地质量等级更新评价等,都为耕地资源承载力的研究提供了数据和现实支撑。
目前,单纯进行耕地资源承载力的研究相对较少,只有少数学者对耕地资源承载力进行了研究。其中具有代表性的有:封志明[5]、高岩[58]、熊平生等[59]、谢平等[60]、张贵军等[61]、郭杰等[62]。这些学者们对耕地资源承载力的定义、计算方法、研究目标等做了初步的探索性研究。其中,封志明[5]从粮食的现实生产力和作物潜在生产力的估算入手,描述了耕地资源承载力的定义,并预测了耕地可承载的人口数量;高岩[58]则将耕地资源承载力定义为一个地区在保证农业生态向良性循环演变条件下,其耕地在一定的生产能力和消费水平下所能承载的最大人口数量,并分析预测了2000年山东耕地生产能力及人口的发展趋势和消费水平;熊平生等[59]通过确定并计算土壤有效系数和社会有效系数,得到耕地社会生产潜力,运用“机制法”的理论探讨重庆地区耕地人口承载力问题;张贵军等[61]对以石家庄市的耕地资源现实粮食生产潜力和可承载的人口数量进行了评价,运用灰色关联模型对耕地面积和人口数量进行了预测;郭杰等[62]认为耕地资源承载力的测算主要是对粮食产能进行评估,粮食生产主要受气候自然条件、土地因素影响,同时还受到要素投入和种植偏好等影响。这些因素的综合作用决定了村域的粮食产能,进而影响到以粮食生产为表征的耕地资源承载力。
由以上研究可见,耕地生产潜力、耕地人口承载数量、耕地粮食产能是耕地资源承载力的主要研究内容,而其中针对人口数量的动态化预测以及保障粮食安全的研究更是其中的重点。
2 关键影响因素识别就目前已有的承载力研究成果和研究方法而言,承载力的研究对象大部分是复杂多变的系统类事物。如:水资源系统、生态系统、耕地资源系统、土地资源系统、环境系统等,这意味着承载力的研究对于资源系统的可持续性有着重要的影响,并且资源系统内部的影响因素之间的相互作用、外部因素对资源系统造成的影响也会使某个资源系统的承载力发生变化,两者是耦合的关系。故在选取评价方法同时,应关注承载力关键影响因素识别方面的可行性,减少因影响因素的不适用使承载力评估效果不佳的情况出现。
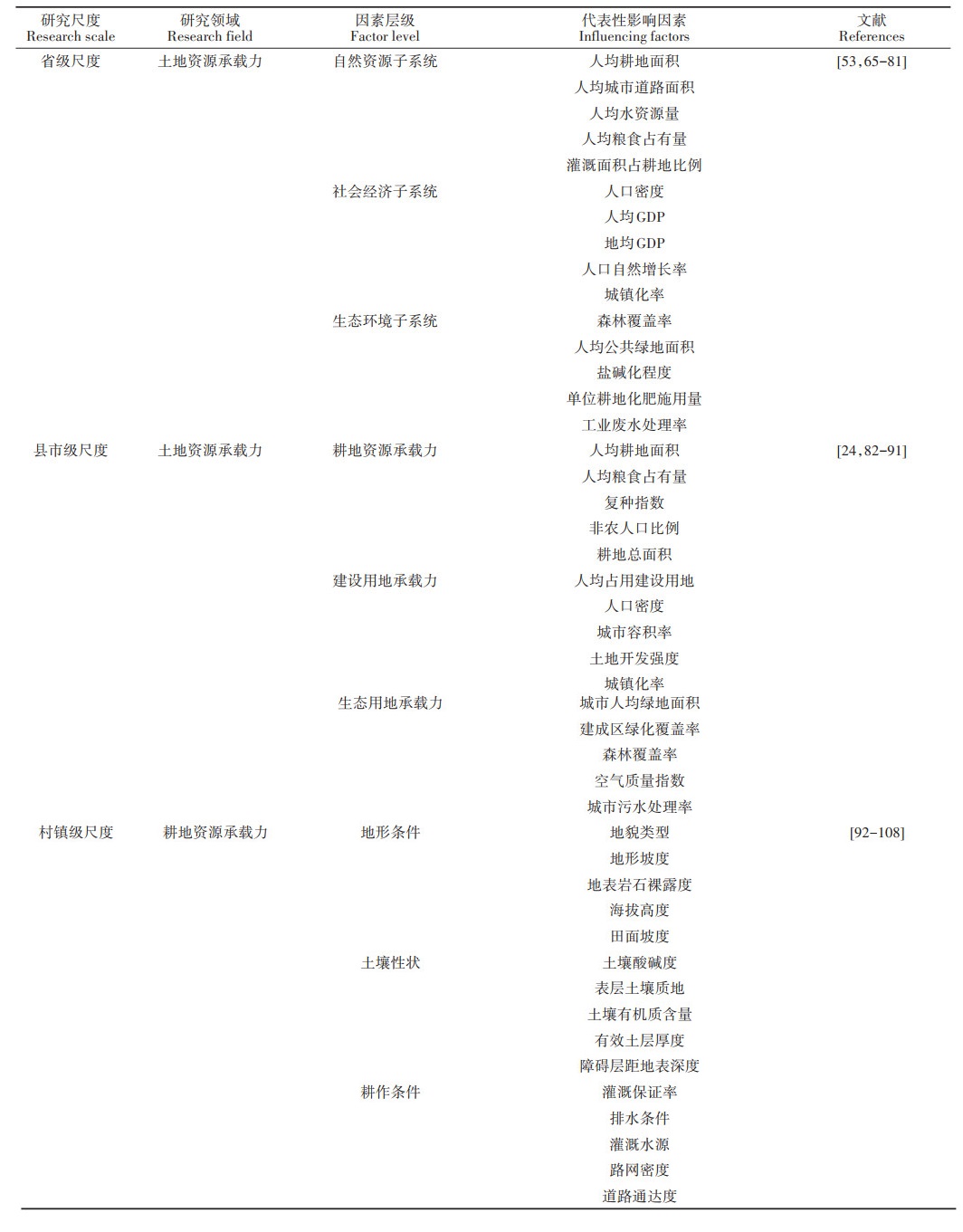
2.1 影响因素评价指标体系影响因素是指在自然资源、社会经济等系统中对耕地资源承载力具有影响能力的要素,可以分为驱动因素(正影响因素)与障碍因素(负影响因素)。驱动因素与障碍因素都会对承载力的承载状态造成影响,其中的关键影响因素更是导致承载力发生显著变化的主要贡献者[63-64]。在承载力评价过程中,国内外学者通过对承载力系统内部的机理分析,从不同的角度构建了耕地资源承载力的影响因素体系。根据对以往相关文献的分析,使用频度统计法,本文统计了影响因素体系中各类型下被选取频率位于前五的代表性影响因素(表 1)。
|
|
表 1 影响因素归纳分类表 Table 1 Summary and classification of influencing factors |
根据研究的空间尺度不同,耕地资源承载力的影响因素具有以下的分类特征:
(1)从省级尺度来看,通常很少进行耕地资源承载力的研究,主要是以土地资源承载力研究为主。省级尺度研究对象的土地资源承载力影响因素指标体系中,一般将承载力分解成各类子系统,由子系统构成一级指标,再由分属于各子系统下影响因素构成二级指标。比如可以根据所采用的不同评价方法,拆解为自然资源、社会经济、生态环境子系统;驱动力子系统、压力子系统、状态子系统以及影响子系统;经济社会、土地资源、生态环境以及科教管理子系统等。而子系统内的指标则可以选择人均GDP、工业废水处理率、人均耕地面积、公共绿地面积、城镇化率等[65-67]。
(2)从县市级尺度来看,主要进行城市土地资源承载力的研究,并且将耕地资源承载力作为城市土地资源承载力的一个分类评价指标。如在县市级尺度研究对象的承载力影响因素指标体系中,土地资源承载力大致由三个一级指标表征,分别是耕地资源承载力、建设用地承载力、生态用地承载力,以这三个一级指标为基础,可使用人均耕地面积、人均建设用地、人均粮食占有量等二级指标计算一级指标(如耕地)的生产潜力或承载能力。综合一级指标的计算结果,评价得出县市尺度的土地资源承载力[82-84]。
(3)从村镇级尺度来看,大部分研究采用土地资源承载指数对小尺度地貌单元的土地资源承载力进行评价[26, 92-94]。而目前村镇尺度的耕地资源承载力评价,其本质是针对耕地资源质量的评价,主要考察自然因素,对影响耕地资源承载力的其他因素,如农户行为因素、社会经济因素等考虑不足[95-98]。所以,村镇尺度上的耕地资源承载力影响因素体系研究仍留有较大的进步与发掘空间。
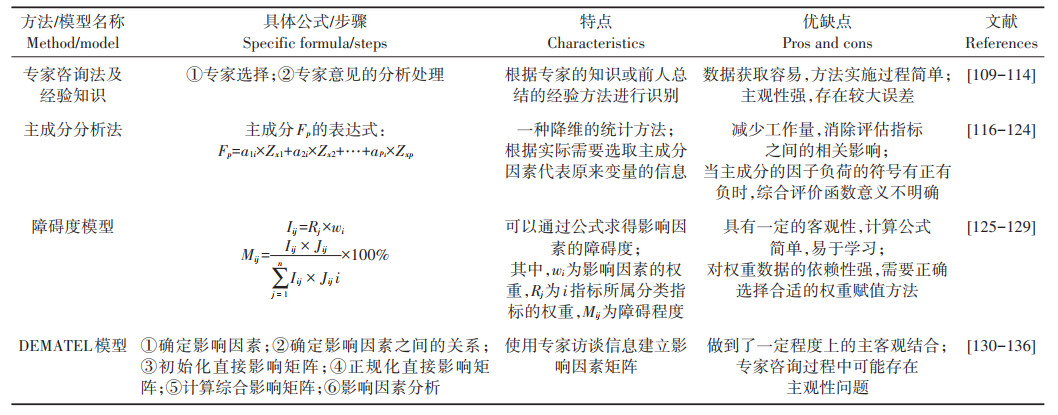
2.2 关键影响因素识别方法影响因素指标体系的建立是对承载力进行表征,而关键影响因素识别则是对承载力系统运作机制的深层次理解。识别关键影响因素,对关键影响因素进行约束或提高,可以显著地改变承载力的承载水平。关键影响因素的识别方法主要分为:(1)专家咨询法以及经验知识;(2)主成分分析法;(3)障碍度模型;(4)DEMATEL(Decision - making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory)模型(表 2)。其中,专家咨询法以及经验知识主要通过借鉴文献资料、他人研究成果和专家打分等方式识别关键影响因素[109-111];主成分分析法是将原来多个指标化为少数几个综合指标的一种统计分析方法[115],使用主成分分析法可以定量分析影响承载力变化的主要驱动因素[48, 116-118];计算影响因素的障碍度,需要引入因子贡献度、指标偏离度以及障碍度三个变量,根据障碍度模型得出每个影响因素的障碍程度,进而识别出关键影响因素[67, 125-126];DEMATEL模型充分利用了专家经验与知识,通过专家访谈的信息建立影响因素直接影响矩阵,进而计算综合影响矩阵,得出各指标的中心度和原因度,完成关键影响因素的识别[130-131]。
|
|
表 2 影响因素识别方法分类 Table 2 Classification of influencing factors identification methods |
总体而言,专家咨询法计算简单,数据处理和结果获取都比较容易,但是存在主观性强的缺陷,在人为因素不可控的情况下,误差较大;主成分分析法与障碍度模型客观性强,识别效果较好,但数据处理繁琐,对数据的精度要求高,依赖性强;DEMATEL模型结合了影响因素矩阵并对专家咨询信息转化,做到了一定程度上的主客观结合。
3 典型评价模型从承载力概念的提出到应用,20世纪20年代以来国内外对承载力的研究方兴未艾,而关于承载力评价方法的研究更是多如繁星。在土地以及耕地资源承载力的研究成果中,可总结出四种典型的主流土地资源承载力评价模型方法,分别是:AEZ(农业生态区)法、生态足迹法、模型指数法与综合评价法。
3.1 AEZ(农业生态区)法农业生态区(Agro-Ecological Zone,AEZ)法是1976年卡萨姆为联合国粮农组织的农业生态区项目制定的计算作物光温生产潜力的方法[137],由荷兰学者Pierre的概念发展而来[5],是联合国粮农组织专门用于研究发展中国家的土地潜在人口承载能力的方法。AEZ法提出之后便迅速应用到非洲、南美洲、东南亚等国家的土地资源承载能力的研究中,AEZ法于20世纪80年代引入中国,最具代表性的研究项目是“中国土地资源生产能力及人口承载量研究”。该项目从土地、粮食、人口之间的关系出发,讨论了土地的限制性,提出了提高土地承载力的主要措施[36]。时至今日,AEZ法已成为世界上应用范围最广的一个农业潜力评估模型[138]。
AEZ法的操作原理是根据土壤、地形和气候的分布将研究区域划分为逻辑分区。这些逻辑分区被称为农业生态区,生态区内土地的自然生产潜力是相似的[139]。采用AEZ法对耕地生产潜力进行估算,需要经过对光合生产潜力、光温生产潜力、气候生产潜力等参数的计算和系数的订正[138, 140],计算公式为:
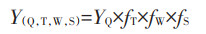
|
(1) |
式中:Y(Q,T,W,S)是作物生产潜力;YQ是光合生产潜力,即某种标准作物的干物质总产量(kg∙hm-2∙d-1);fT为假设除光和温度外,其他因素都处于理想状态的光温生产潜力;fW为水分订正系数,气候生产潜力就是在光温生产潜力的基础上乘以水分订正系数;fS为土壤修正系数,根据土壤质量评价结果确定。
农业生态区法的实际研究中,谢俊奇等[141]根据中国的特点改进了AEZ法,并将其应用到全国的耕地粮食生产潜力评价的实践中,得出AEZ法是宏观尺度下土地生产潜力的有效评价方法这一结论;蔡成凤等[142]基于淮海市的沿海地理特征,对方法中的订正系数进行了符合当地实际情况的更改,为AEZ方法在更多特殊地区的应用提供了参考;王连喜等[143]运用AEZ模型得出冬小麦生产潜力的产量差,研究气候变化背景下,不同限制因素对小麦产量提高的限制作用,利用AEZ模型揭示了气温、降水、土壤等因素对耕地生产潜力的影响。
AEZ法通过计算光合生产潜力、光温生产潜力等作物的本底生产潜力,从自然因素的角度入手,对耕地生产潜力进行了计算。AEZ法引进中国后,许多学者们都对其进行了参数上的修改,使其能够适应中国的自然资源条件[141, 144-145],但只有极少数研究考虑了经济因素对耕地生产潜力的影响。总体上来看,AEZ法的优点是:AEZ法计算简单,所需的数据量少并且数据容易获取。缺点是:在地域差异明显、气候条件多变的国家则会面临普适性差的问题,而且面对过于复杂的承载力系统时,参数过多,计算过程会变的复杂[139]。
3.2 生态足迹法生态足迹(Ecological Footprint)理论最初由Rees[29]于1992年提出,之后Wackernagel等[146]对该理论的计算方法及原理进行了发展和完善。生态足迹法的原理核心可以归结为两点:(1)人类的资源消耗和废物排放会在生态环境中留下“足迹”可供追溯;(2)而维持资源消耗的是生物生存的原始生物区,并且生物区提供的资源是有限的。所以通过对比人类对自然的消耗量与自然资本的承载量,可以判断研究区域生态系统的承载状况[147]。生态足迹理论的提出,提供了一个从供需关系进行承载力研究的新视角,也因为生态足迹模型着眼于宏观层面的资源消耗和承载,这使其能在众多资源承载力领域得到普遍应用。生态足迹模型的计算步骤可分为主要的三步:(1)将各类能源消耗行为折算为不同土地类型和土地平均生产率下的生物生产面积;(2)为消除不同生物之间的差异,将各类生物的生产面积乘以一个均衡因子,得到相同生态生产力的人均生物生产面积;(3)均衡处理后各类系统的人均生物生产面积相加,得到生态足迹。公式为:
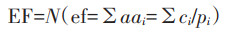
|
(2) |
式中:i为各类能源消耗行为;pi为各类能源的平均生产能力;ci为i类能源的人均消费量;aai为人均i类能源折算的生产土地面积;N为人口数;ef为人均生态足迹;EF为总的生态足迹。
在实际应用研究中,刘东等[148]应用生态足迹模型构建了生态承载力供需平衡指数,从县域尺度评价了我国生态承载力的供需平衡状态;张红等[149]针对舟山市作为海岛城市的资源环境特点,对生态足迹模型做出如下改进:(1)引入新的消耗资源类型,如淡水资源;(2)根据研究区陆地面积的大小,更改特定用地的生物生产面积,之后使用该改进模型评估了舟山市的土地承载力。
在应用过程中可以看出,生态足迹法的优点是:(1)生态足迹模型紧扣可持续发展理论,是一个综合性的指标,符合承载力研究中对于可持续性的要求;(2)提供了一个新的承载力供需平衡研究视角,可以一定程度上反映社会经济发展和自然资源承载能力之间的盈余情况[149]。缺点是:不能对自然环境中提供的能源描述完全,如地下水资源和某些自然存量[139]。
3.3 模型指数法模型指数法是指根据研究区域、研究对象和数据基础的特点,选择合适的模型或者指数,将其用于承载力的计算。模型指数法是各类模型与指数公式的合集总称,承载力领域中最常使用的代表性模型和指数有:系统动力学模型(System Dynamic,SD)、灰色系统模型GM(1,1)、多目标决策模型[42]、土地承载指数、承载状态指数等,本文主要介绍系统动力学模型和土地资源承载指数。
系统动力学理论方法由1956年麻省理工学院的Forrester教授[150]创立。系统动力学理论综合了信息论、控制论、系统知识以及计算机仿真模拟技术,以系统中的反馈控制理论为基础,可以准确地模拟和把握系统间各因素的相互作用和影响机制,是研究系统类问题的利器[151]。系统动力学于20世纪70年代末引入中国,经过近百年的发展,系统动力学的应用已深入涉及到社会、经济、自然等领域的资源预测、管理、优化和可持续发展的研究中[152]。系统动力学理论在承载力领域中最具代表性的研究是1980年代初期由英国科学家Slessor教授通过使用系统动力学方法设计的ECCO(承载能力选择)模型,该模型用于模拟人口变化与承载力之间的关系,并在非洲做了实际应用研究[33, 36]。目前,在承载力研究方面系统动力学模型的应用成果有:Wei等[153]针对城市生态系统这样一个具有复杂反馈的动态系统,使用系统动力学模型测度城市生态承载力;在不同的控制情景下,基于系统动力学模型,预测农产品生产与经济指数变化趋势,以此评估农村居民点的土地资源人口承载力[49];杨子江等[154]同样根据水资源系统复杂多变的特征,设置了五种不同的社会发展类型方案,利用系统动力学模型模拟不同方案下水资源系统的动态变化。
土地资源承载指数是一种基于人-粮关系建立的评价土地资源承载力的指数模型,该模型由封志明等[26]提出并构建。土地资源承载指数实际上是现实人口承载数量与土地资源承载力的比值,揭示了实际人口与承载能力的相互关系,其中,土地资源承载力被定义为粮食总量与人均粮食消费标准的比值,代表着一定粮食消费水平下,研究区粮食产量能供养的人口规模,具体公式:
土地资源承载力(LCC):
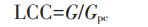
|
(3) |
式中:LCC为土地资源承载力,人;G为粮食总产量,kg;Gpc为人均粮食消费标准,kg·人-1。
土地资源承载指数:
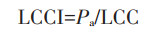
|
(4) |
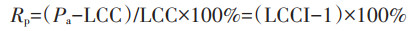
|
(5) |
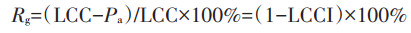
|
(6) |
式中:LCCI为土地资源承载指数;Pa为现实人口数量,人;Rp为人口超载率;Rg为粮食盈余率。
之后的研究中,许多学者对土地承载力指数模型进行了应用和改进:谢平等[60]从人粮关系的视角计算了耕地资源人口承载力,通过更改土地承载力指数比值结果的表征意义,利用土地承载力指数表征了耕地资源人口承载力;全江涛等[48]对指数模型进行了改进,添加了土地资源限制度模型,在计算土地资源承载力的基础上,进一步掌握了土地资源视角下的人口的数量、限制和分布特征。模型指数法的优点是客观性强、易于解决系统问题且评价结果准确性较高;缺点是模型指数法对数据的要求较高,并且需要研究者对研究的承载力系统有足够的了解,才能选择合适的模型。
3.4 综合评价法自承载力引入资源环境领域学科的研究之后,随着社会经济发展、人为活动日益频繁、自然灾害频发、能源资源衰竭等问题的不断出现,生物的生存环境开始变得复杂,承载力研究对象及其影响因素的复杂程度也逐步攀升[139]。学者们发现,只有少数影响因子参与运算的计算模型和仅基于简单数学关系的指数公式已经无法完整地反映和揭示承载力系统中日益复杂的各类影响因素之间的关系[155-156]。因此学者们开始寻求一种更为全面、系统的承载力评价测算方法,使综合评价法成为了承载力研究发展的新趋势。
徐永胜[157]在探讨土地人口承载力的性质和影响因素时将指标体系引入了研究中,认为土地对人口的承载力是由各类影响因素构成的指标共同影响的,该研究是综合评价法在承载力领域应用的最初尝试。20世纪90年代后,综合评价法迎来了蓬勃的发展,各式各样基于评价指标体系的研究开始涌现:一些学者将综合评价法与一种模型或方法相结合,如系统动力学模型、优化投影寻踪模型、均方差决策法、供需平衡指数等,以改进评价指标体系中主观性成分较大的缺点[158-161];或者以评价指标体系为基础,将承载力研究过程中求解各类复杂关系的模型进行分组模块化,纳入以评价指标体系为主干的综合集成框架中,对整个研究对象进行全方位、流程化、全面性的评估,从而达到优化承载力评价指标体系结果、提高评估精度的目的[162-166]。
综合评价法可以将各方面因素综合起来,再结合各类方法进行评价,评价结果更加全面,适合承载力这类十分复杂系统研究;但仍存在缺陷,综合评价法在小尺度上无法获取到足够的基础数据,且评价过程中的权重确定也容易受到主观因素的影响。
综上所述,以上4类典型评价模型在耕地资源承载力评价中的应用具有以下特征:(1)生态足迹法和AEZ法适用于数据量少、影响因素较少,宏观尺度的承载力计算;(2)模型指数法与综合评价法适用于数据量中等或较大、影响因素复杂多样的承载力综合评价;(3)根据对比结果,本文建议综合考虑4种方法的优缺点,将生态足迹法、AEZ法、模型指数法与综合评价法相结合,形成一个综合的集成评价框架,以评价指标体系为主干,前三者可作为框架中的一个子处理过程。总而言之,多种评价方法集成的综合评价将是承载力未来发展的重要趋势。
4 讨论耕地资源对于各个国家和地区都是十分珍贵和稀缺的生产资料。我国在改革开放之前,对耕地资源的保护方面重视程度不够;改革开放之后,社会经济飞速发展,使得国内耕地资源利用结构发生了改变,相继制定、颁布了一系列耕地保护政策。然而耕地资源保护与利用的效果不尽如人意,耕地数量的减少速度虽然得到了控制,城市建设项目占用耕地的压力仍然存在,耕地污染和耕地质量下降等问题仍较为严峻。耕地资源承载力的研究有助于我国现行和未来耕地保护政策的优化。
2020年以来,全球经济生产出现了短期停滞,加之东非的蝗灾、席卷全球的旱灾等自然灾害,世界各大产粮国粮食歉收,全球粮食将减产达30%[167],粮食危机近在眼前。中国人多地少,人地矛盾尖锐,粮食安全是首要的问题。耕地资源承载力研究以粮食安全为标准,以测算适度的粮食产能和人口的可持续承载数量为目标,通过对耕地资源承载力进行有效、合理、精确的评价,可以科学地找出最优的耕地资源承载力提升路径,为耕地保护相关政策提供科学、客观的数据参考,发掘在当前耕地质量与利用效率下,保证粮食安全所需的粮食生产规模以及产量。
5 结论本文详述了目前土地资源承载力、耕地资源承载力的研究进展,回顾和对比了两类承载力的评价模型,包括对承载力中关键影响因素的识别方式的总结梳理。耕地资源承载力研究涉及到各类影响因素筛选与识别、评价体系的构建、评价模型选取等步骤,但目前研究中并未形成一个综合完善的框架,现有研究中存在以下问题:
(1)耕地资源承载力关键因素识别方法的成果还相对较少,实际应用中容易降低评价结果的有效性。
(2)耕地资源承载力的评价体系具有系统特征,影响因素具有空间尺度上的特征。而现有的评价模型方法缺乏对耕地资源承载力系统性、空间性的综合考量,且在村镇尺度上存在一定的研究空白,今后在研究方法选择上应优先考虑综合评价模型。
(3)以往的研究多着重于对人口极限承载容量的确定。但是随着人类社会科技的进步,工业与交通体系的日益完善,经济贸易的发达,地区间人口流动十分频繁,在未来的研究中,追求土地资源的极限人口承载容量将失去意义。研究应集中在粮食安全的保障和人口的可持续性承载上,对耕地资源承载力进行更全面综合的评价。
| [1] |
Shen L Y, Ren Y T, Xiong N, et al. Why small towns can not share the benefits of urbanization in China?[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 174(10): 728-738. |
| [2] |
Bai X M, Shi P J, Liu Y S. Society:Realizing China's urban dream[J]. Nature, 2014, 509(7501): 423. DOI:10.1038/509423a |
| [3] |
German R N, Thompson C E, Benton T G. Relationships among multiple aspects of agriculture's environmental impact and productivity:A meta-analysis to guide sustainable agriculture[J]. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 2017, 92: 716-738. DOI:10.1111/brv.12251 |
| [4] |
Oliver M A, Gregory P J. Soil, food security and human health:A review[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2014, 66(2): 257-276. |
| [5] |
封志明. 贵州省耕地承载力研究[J]. 自然资源, 1992(4): 35-41. FENG Zhi-ming. Study on the carrying capacity of cultivated land in Guizhou Province[J]. Natural Resources, 1992(4): 35-41. |
| [6] |
杨国义, 钟继洪, 林美莹, 等. 广东耕地资源的人口承载力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2000(2): 103-105. YANG Guo-yi, ZHONG Ji-hong, LIN Mei-ying, et al. Study on population carrying capacity of cultivated land resources in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2000(2): 103-105. |
| [7] |
胡新艳, 刘一明, 牛宝俊. 东南沿海地区耕地资源承载力研究[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2001(1): 21-24. HU Xin-yan, LIU Yi-ming, NIU Bao-jun. Study on the carrying capacity of cultivated land resources in southeast coastal areas[J]. Research on Land and Natural Resources, 2001(1): 21-24. |
| [8] |
景跃军, 陈英姿. 关于资源承载力的研究综述及思考[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2006(5): 11-14. JING Yue-jun, CHEN Ying-zi. Review and thinking on the research of the resources carrying capacity[J]. China Population Resources and Environment, 2006(5): 11-14. |
| [9] |
张燕, 徐建华, 曾刚, 等. 中国区域发展潜力与资源环境承载力的空间关系分析[J]. 资源科学, 2009(8): 68-74. ZHANG Yan, XU Jian-hua, ZENG Gang, et al. The spatial relationship between regional development potential and resource & environment carrying capacity[J]. Resources Science, 2009(8): 68-74. |
| [10] |
吴琼. 基于因子分析的青海省水资源承载力综合评价[J]. 水资源保护, 2013, 29(1): 22-26. WU Qiong. Comprehensive evaluation of carrying capacity of water resources of Qinghai Province based on factor analysis[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2013, 29(1): 22-26. |
| [11] |
施开放, 刁承泰, 孙秀锋. 基于熵权可拓决策模型的重庆三峡库区水土资源承载力评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(2): 609-616. SHI Kai-fang, DIAO Cheng-tai, SUN Xiu-feng. Evaluation of soilwater resources carrying capacity based on entropy weight extension decision model in the Three Gorges Reservoir region of Chongqing[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(2): 609-616. |
| [12] |
郑大同. 地基极限承载力的计算[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1979: 1-2. ZHENG Da-tong. Calculation of ultimate bearing capacity of foundation[M]. Beijing: China Architecture Buiding Press, 1979: 1-2. |
| [13] |
Verhulst P F. Notice sur la loi que la population suit dans son accroissement[J]. Correspondance Mathématique Physique, 1838, 10: 113-121. |
| [14] |
Hardin G. AIBS News:Cultural carrying capacity:A biological approach to human problems[J]. Bio Science, 1986, 36(9): 599-605. |
| [15] |
Park R F, Burgoss E W. An introduction to the science of sociology[M]. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press, 1921.
|
| [16] |
Odum E P. Fundamentals of ecology[J]. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club, 1955, 82(5): 400. DOI:10.2307/2482488 |
| [17] |
Dhondt A A. Carrying capacity:A confusing concept[J]. Acta Oecologica/Oceologia Generalis, 1988, 9(4): 337-346. |
| [18] |
Price D. Carrying capacity reconsidered[J]. Population and Environment, 1999, 21(1): 5-26. |
| [19] |
Clarke A L. Assessing the carrying capacity of the Florida Keys[J]. Population & Environment, 2002, 23(4): 405-418. |
| [20] |
Graymore M.Journey to Sustainability: Small regions, sustainable carrying capacity and sustainability assessment methods[D].Brisbane: Griffith University, 2005: 24-77.
|
| [21] |
Errington P L. Vulnerability of bobwhite populations to predation[J]. Ecology, 1934, 15(2): 110-127. DOI:10.2307/1932781 |
| [22] |
Arrow K, Bolin B, Costanza R, et al. Economic growth, carrying capacity, and the environment[J]. Science, 1995, 268(5210): 520-521. DOI:10.1126/science.268.5210.520 |
| [23] |
新疆水资源软科学课题研究组. 新疆水资源及其承载能力和开发战略对策[J]. 水利水电技术, 1989(6): 2-9. Xinjiang Water Resources soft Science Research Group. Water resources, carrying capacity and development strategy of Xinjiang[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 1989(6): 2-9. |
| [24] |
朱祥明. 黄淮海平原耕地资源承载力的研究——以安徽淮北亳州、涡阳、蒙城、怀远为例[J]. 资源科学, 1992(1): 13-20, 12. ZHU Xiang-ming. Study on the carrying capacity of cultivated land resources in Huang Huai Hai Plain[J]. Resources Science, 1992(1): 13-20, 12. |
| [25] |
崔凤军. 论旅游环境承载力——持续发展旅游的判据之一[J]. 经济地理, 1995(1): 105-109. CUI Feng-jun. Study on tourist environmental bearing capacity[J]. Economic Geography, 1995(1): 105-109. |
| [26] |
封志明, 杨艳昭, 张晶. 中国基于人粮关系的土地资源承载力研究:从分县到全国[J]. 自然资源学报, 2008(5): 865-875. FENG Zhi-ming, YANG Yan-zhao, ZHANG Jing. The land carrying capacity of China based on man-grain relationship[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2008(5): 865-875. |
| [27] |
陈春生. 环境容量受力分析与都市成长管理之研究——以台北都会区水资源个案为例[J]. 国立台湾大学建筑与城乡研究学报, 1987, 3(1): 133-134. CHEN Chun-sheng. Environmental carrying capacity analysis and growth management[J]. Bulletin of Architecture and City Planning National Taiwan University, 1987, 3(1): 133-134. |
| [28] |
徐大海, 王郁. 确定大气环境承载力的烟云足迹法[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(6): 1734-1740. XU Da-hai, WANG Yu. Plume footprints analysis for determining the bearing capacity of atmospheric environment[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiate, 2013, 33(6): 1734-1740. |
| [29] |
Rees W E. Ecological footprints and appropriated carrying capacity:What urban economics leaves out[J]. Environment & Urbanization, 1992, 4(2): 121-130. |
| [30] |
王中根, 夏军. 区域生态环境承载力的量化方法研究[J]. 长江工程职业技术学院学报, 1999(4): 9-12. WANG Zhong-gen, XIA -Jun. Quantitative analysis on bearing capacity of ecological environment[J]. Journal of Changjiang Vocational University, 1999(4): 9-12. |
| [31] |
Seidl I, Tisdell C A. Carrying capacity reconsidered:From Malthus' population theory to cultural carrying capacity[J]. Ecological Economics, 1999, 31(3): 395-348. DOI:10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00063-4 |
| [32] |
Australian UNESCO Seminar, Australian UNESCO Committee for Man and the Biosphere. Energy and how we live[M]. Canberra: Australian UNESCO Committee, 1973: 16-18.
|
| [33] |
UNESCO & FAO.Carrying capacity assessment with a pilot study of Kenya: A resource accounting methodology for exploring national options for sustainable development[R].Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 1985.
|
| [34] |
阮本青, 沈晋. 区域水资源适度承载能力计算模型研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 1998(3): 3-5. RUAN Ben-qing, SHEN Jin. Research on calculation model of regional water resources moderate carrying capacity[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 1998(3): 3-5. |
| [35] |
陈念平. 土地资源承载力若干问题浅析[J]. 自然资源学报, 1989(4): 371-380. CHEN Nian-ping. A preliminary analysis of the population supporting capacity of land resources[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 1989(4): 371-380. |
| [36] |
封志明. 土地承载力研究的过去、现在与未来[J]. 中国土地科学, 1994(3): 1-9. FENG Zhi-ming. The past, present and future of land carrying capacity research[J]. China Land Science, 1994(3): 1-9. |
| [37] |
林玉标. 芜湖市耕地承载力初步研究[J]. 华东经济管理, 1999(4): 3-5. LIN Yu-biao. Preliminary study on the carrying capacity of cultivated land in Wuhu City[J]. East China Economic Management, 1999(4): 3-5. |
| [38] |
崔侠, 姚艳敏, 何江华. 广州市东部地区土地资源承载力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2003(1): 42-45. CUI Xia, YAO Yan-min, HE Jiang-hua. Bearing capacity of land resources in the eastern district of Guangzhou City[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2003(1): 42-45. |
| [39] |
罗雁文, 魏晓, 王良健, 等. 湖南省各市(州)土地资源承载力评价[J]. 经济地理, 2009, 29(2): 284-289. LUO Yan -wen, WEI Xiao, WANG Liang-jian, et al. Land carrying capacity in the states of Hunan Province[J]. Economic Geography, 2009, 29(2): 284-289. |
| [40] |
刘晓丽, 方创琳. 城市群资源环境承载力研究进展及展望[J]. 地理科学进展, 2008(5): 35-42. LIU Xiao-li, FANG Chuang-lin. Research progress and prospect of urban agglomeration resources and environment carrying capacity[J]. Progress in Geography, 2008(5): 35-42. |
| [41] |
Allan W. The African husbandman[M]. Edinburg: Oliver and Boyd, 1965.
|
| [42] |
Millington R, Gifford R.Energy and how we live[R].Ganberra Australian UNESO Seminar Committee to Man and Biosphere, 1973.
|
| [43] |
吴殿廷. 区域经济学[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 26-27. WU Dian-ting. Regional economics[M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 26-27. |
| [44] |
F AO. Potential population supporting capacities of lands in the developing world[M]. Rome: FAO, 1982: 23-27.
|
| [45] |
陈百明. "中国土地资源生产能力及人口承载量"项目研究方法概论[J]. 自然资源学报, 1991(3): 197-205. CHEN Bai-ming. An outline of the research method of the project "the productivity and population carrying capacity of the land resource in china"[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 1991(3): 197-205. |
| [46] |
郑振源. 中国土地的人口承载潜力研究[J]. 中国土地科学, 1996, 10(4): 33-38. ZHENG Zhen-yuan. Research of potential population carrying capacity of Chinese land[J]. China Land Science, 1996, 10(4): 33-38. |
| [47] |
陈百明. 中国农业资源综合生产能力与人口承载能力[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2001: 1-58. CHEN Bai-ming. The comprehensive productivity and population carrying capacity of the agricultural resources in China[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2001: 1-58. |
| [48] |
全江涛, 杨永芳, 周嘉昕. 河南省土地资源承载力时空演变分析与预测[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(2): 315-322. QUAN Jiang-tao, YANG Yong-fang, ZHOU Jia-xin. Analysis and prediction of spatial and temporal evolution of land resource carrying capacity in Henan Province[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(2): 315-322. |
| [49] |
Guo S L, Li C J, Liu S Q, et al. Land carrying capacity in rural settlements of Three Gorges Reservoir based on the system dynamic model[J]. Natural Resource Modeling, 2018, 31(2): e12152. DOI:10.1111/nrm.12152 |
| [50] |
陈芳淼, 田亦陈, 袁超, 等. 基于供给生态服务价值的云南土地资源承载力评估方法研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(12): 1605-1613. CHEN Fang-miao, TIAN Yi-chen, YUAN Chao, et al. Methods of land carrying capacity research based on ecological services supply value in Yunnan[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2015, 23(12): 1605-1613. |
| [51] |
史娜娜, 全占军, 韩煜, 等. 基于生态敏感性评价的乌海市土地资源承载力分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(1): 239-243. SHI Na-na, QUAN Zhan-jun, HAN Yu, et al. Analysis of land resources carrying capacity in Wuhai City based on ecological sensitivity[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 24(1): 239-243. |
| [52] |
Tsou J, Gao Y, Zhang Y, et al. Evaluating urban land carrying capacity based on the ecological sensitivity analysis:A case study in Hangzhou, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(6): 529. DOI:10.3390/rs9060529 |
| [53] |
姜秋香, 付强, 王子龙. 基于粒子群优化投影寻踪模型的区域土地资源承载力综合评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(11): 319-324. JIANG Qiu-xiang, FU Qiang, WANG Zi-long. Comprehensive evaluation of regional land resources carrying capacity based on projection pursuit model optimized by particle swarm optimization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 27(11): 319-324. |
| [54] |
封志明, 杨艳昭, 闫慧敏, 等. 百年来的资源环境承载力研究:从理论到实践[J]. 资源科学, 2017, 39(3): 379-395. FENG Zhi-ming, YANG Yan-zhao, YAN Hui-min, et al. A review of resources and environment carrying capacity research since the 20th Century:From theory to practice[J]. Resources Science, 2017, 39(3): 379-395. |
| [55] |
孙友然, 贾愚, 江游. 江苏省耕地资源劳动力承载力研究[J]. 科技管理研究, 2008(6): 156-158. SUN You-ran, JIA Yu, JIANG You. Study on the labor carrying capacity of cultivated land resources in Jiangsu Province[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2008(6): 156-158. |
| [56] |
王玉军, 刘存, 周东美, 等. 客观地看待我国耕地土壤环境质量的现状——关于《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》中有关问题的讨论和建议[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(8): 1465-1473. WANG Yu-jun, LIU Cun, ZHOU Dong-mei, et al. A critical view on the status quo of the farmland soil environmental quality in China:Discussion and suggestion of relevant issues on Report on the National General Survey of Soil Contamination[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(8): 1465-1473. |
| [57] |
毋晓蕾, 郑金叶.农用地产能核算研究[C]//第七届全国地理学研究生学术年会论文摘要集.中国地理学会, 2012: 66. WU Xiao-lei, ZHENG Jin-ye.Research on agricultural land productivity accounting[C]//Abstracts of theses of the 7th national geographic graduate conference.China Geography Society, 2012: 66. |
| [58] |
高岩. 山东省2000年耕地承载力研究[J]. 地域研究与开发, 1997(4): 67-70. GAO Yan. Study on Bearing the weight of plough of Shandong Province of 2000 Year[J]. Areal Research and Development, 1997(4): 67-70. |
| [59] |
熊平生, 谢金宁, 谢世友. 重庆地区耕地生产潜力及承载力分析[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2008(5): 584-587. XIONG Ping-sheng, XIE Jin-ning, XIE Shi-you. Productive latent capacity of cultivated land and load support capability in Chongqing region[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2008(5): 584-587. |
| [60] |
谢平, 文倩, 孙水娟, 等. 基于人粮关系的湖南省耕地资源人口承载力研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 2012, 19(4): 274-277, 295. XIE Ping, WEN Qian, SUN Shui-juan, et al. Research on cultivated land carrying capacity based on human-grain relationship in Hunan Province[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 19(4): 274-277, 295. |
| [61] |
张贵军, 朱永明, 张蓬涛, 等. 石家庄市耕地资源人口承载力评价[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2013, 34(6): 120-126. ZHANG Gui-jun, ZHU Yong-ming, ZHANG Peng-tao, et al. Evaluation on population carrying capacity of cultivated land in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2013, 34(6): 120-126. |
| [62] |
郭杰, 陈鑫, 赵雲泰, 等. 乡村空间统筹治理的村庄规划关键科学问题研究[J]. 中国土地科学, 2020, 34(5): 76-85. GUO Jie, CHEN Xin, ZHAO Yun-tai, et al. Research on the key scientific questions of village planning based on rural spatial comprehensive governance[J]. China Land Science, 2020, 34(5): 76-85. |
| [63] |
周智, 黄英, 黄娟. 水土资源承载力区域差异与影响因素[J]. 水土保持通报, 2015, 35(2): 344-349. ZHOU Zhi, HUANG Ying, HUANG Juan. Regional differences and influencing factors of soil-water resources carrying capacity[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 35(2): 344-349. |
| [64] |
郭倩, 汪嘉杨, 张碧. 基于DPSIRM框架的区域水资源承载力综合评价[J]. 自然资源学报, 2017, 32(3): 484-493. GUO Qian, WANG Jia-yang, ZHANG Bi. Comprehensive evaluation of the water resource carrying capacity based on DPSIRM[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2017, 32(3): 484-493. |
| [65] |
Komatsu Y, Tsunekawa A, Ju H. Evaluation of agricultural sustainability based on human carrying capacity in drylands:A case study in rural villages in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2004, 108(1): 1-98. |
| [66] |
何刚, 夏业领, 朱艳娜, 等. 基于DPSIR-TOPSIS模型的安徽省土地承载力评价及预测[J]. 水土保持通报, 2018, 38(2): 127-134. HE Gang, XIA Ye-ling, ZHU Yan-na, et al. Evaluation and prediction of land carrying capacity in Anhui Province based on DPSIRTOPSIS model[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 38(2): 127-134. |
| [67] |
李洁. 长江经济带土地综合承载力时空分异评价与障碍因子诊断[J]. 华东经济管理, 2019, 33(8): 67-75. LI Jie. Spatiotemporal differentiation of land comprehensive carrying capacity and diagnosis of obstacle factors in the Yangtze River economic belt[J]. East China Economic Management, 2019, 33(8): 67-75. |
| [68] |
齐亚曼.河南省耕地生产能力及承载力时空变化研究[D].郑州: 河南财经政法大学, 2019: 22-27. QI Ya-man.Spatial and temporal changes of cultivated land productivity and carrying capacity in Henan Province[D].Zhengzhou: Henan University of Economics and Law, 2019: 22-27. |
| [69] |
高洁宇. 基于生态敏感性的城市土地承载力评估[J]. 城市规划, 2013, 37(3): 39-42. GAO Jie -yu. Assessment on land bearing capacity of city based on ecological sensitivity[J]. City Planning Review, 2013, 37(3): 39-42. |
| [70] |
刘明, 高林. 基于城镇化科学发展的京津冀区域土地资源承载力研究[J]. 城市发展研究, 2015, 22(4): 6-8. LIU Ming, GAO Lin. Based on the research of scientific development of urbanization on Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei's bearing capacity of land resources[J]. Urban Development Studies, 2015, 22(4): 6-8. |
| [71] |
许联芳, 谭勇. 长株潭城市群"两型社会"试验区土地承载力评价[J]. 经济地理, 2009, 29(1): 69-73. XU Lian-fang, TAN Yong. Study on the land carrying capacity of resource-saving and environment-friendly development experimental area in ChangZhuTan megalopolis[J]. Economic Geography, 2009, 29(1): 69-73. |
| [72] |
陈珏, 雷国平, 王元辉. 黑龙江省土地综合承载力空间差异研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2011, 21(增刊): 267-270. CHEN Yu, LEI Guo-ping, WANG Yuan-hui. Spatial differentiation of comprehensive land carrying capacity in Heilongjiang Province[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2011, 21(S1): 267-270. |
| [73] |
李新刚, 王双进, 孙钰. 土地承载力与经济发展的动态效应和耦合协调——基于京津冀城市群的实证研究[J]. 经济理论与经济管理, 2018(12): 98-109. LI Xin-gang, WANG Shuang-jin, SUN Yu. The dynamic effect and coupling coordination of land carrying capacity and economic development:An empirical study based on Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration[J]. Economic Theory and Business Management, 2018(12): 98-109. |
| [74] |
王书华, 曹静. 土地综合承载力评判指标体系的构建及应用[J]. 河北师范大学学报, 2001(1): 129-133. WANG Shu-hua, CAO Jing. Concept and usage of the index system design to the land comprehensive carrying capacity[J]. Journal of Hebei Normal University (Natural Science), 2001(1): 129-133. |
| [75] |
曹月娥.基于GIS的新疆土地综合承载力研究[D].乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2005: 39-55. CAO Yue-e.Study on comprehensive land carrying capacity of Xinjiang based on GIS[D].Urumchi: Xinjiang University, 2005: 39-55. |
| [76] |
李兰图, 陈文宽, 孙丽娜. 江苏省土地综合承载力时空差异分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2011, 18(1): 12-16, 23. LI lan-tu, CHEN Wen-kuan, SUN Li-na. Analysis of temporospatial variations of the land's comprehensive carrying capacity in Jiangsu Province[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 18(1): 12-16, 23. |
| [77] |
任守德, 付强, 王凯. 基于宏微观尺度的三江平原区域农业水土资源承载力[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(2): 8-14. REN Shou-de, FU Qiang, WANG Kai. Regional agricultural water and soil resources carrying capacity based on macro -micro scale in Sanjiang Plain[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 27(2): 8-14. |
| [78] |
于广华, 孙才志. 环渤海沿海地区土地承载力时空分异特征[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(14): 4860-4870. YU Guang-hua, SUN Cai-zhi. Land carrying capacity spatiotemporal differentiation in the Bohai Sea coastal areas[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(14): 4860-4870. |
| [79] |
Luo W Z, Ren Y T, Shen L Y, et al. An evolution perspective on the urban land carrying capacity in the urbanization era of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 744: 140827. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140827 |
| [80] |
Sun M Y, Wang J G, He K Y. Analysis on the urban land resources carrying capacity during urbanization:A case study of Chinese YRD[J]. Applied Geography, 2020, 166: 102170. |
| [81] |
Shao Q L, Liu X C, Zhao W J. An alternative method for analyzing dimensional interactions of urban carrying capacity:Case study of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay area[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 273: e111064. DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111064 |
| [82] |
郭志伟. 北京市土地资源承载力综合评价研究[J]. 城市发展研究, 2008, 15(5): 24-30. GUO Zhi-wei. Comprehensive evaluation on land resources carrying capacity for Beijing City[J]. Urban Studies, 2008, 15(5): 24-30. |
| [83] |
Shi Y S, Wang H F, Yin C Y. Evaluation method of urban land population carrying capacity based on GIS:A case of Shanghai, China[J]. Computers Environment & Urban Systems, 2013, 39(5): 27-38. |
| [84] |
温亮, 游珍, 林裕梅, 等. 基于层次分析法的土地资源承载力评价——以宁国市为例[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2017, 38(3): 1-6. WEN Liang, YOU Zhen, LIN Yu-mei, et al. Evaluation on land carrying capacity:A case of Ningguo City[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2017, 38(3): 1-6. |
| [85] |
郭艳红. 基于均方差分析法的北京市土地资源承载力评价[J]. 资源与产业, 2011, 13(6): 62-66. GUO Yan-hong. Evaluation of Beijing's land resources load capacity based on mean variance analysis[J]. Resources & Industries, 2011, 13(6): 62-66. |
| [86] |
王大本, 刘兵. 京津冀区域土地资源承载力评价研究[J]. 经济与管理, 2019, 33(2): 9-14. WANG Da-ben, LIU Bing. Evaluation research of land resources carrying capacity in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Economy and Management, 2019, 33(2): 9-14. |
| [87] |
谢冲.池州市城市土地资源承载力可持续性评价分析[D].武汉: 华中师范大学, 2012: 15-17. XIE Chong.Sustainability evaluation of urban land resources carrying capacity in Chizhou City[D].Wuhan: Central China Normal University, 2012: 15-17. |
| [88] |
陈书卿, 刁承泰, 常丹青. 统筹城乡发展视角下的重庆市土地资源承载力及农民市民化研究[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2009, 30(5): 547-551. CHEN Shu-qing, DIAO Cheng-tai, CHANG Dan-qing. Research of land resources carrying capacity and farmers' urbanization in perspective of integrated urban and rural development in Chongqing City[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2009, 30(5): 547-551. |
| [89] |
程小于, 杨庆媛, 毕国华. 重庆市江津区土地资源承载力时空差异研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(10): 2319-2330. CHENG Xiao-yu, YANG Qing-yuan, BI Guo-hua. Spatial and temporal differences of land resources carrying capacity in Jiangjin District of Chongqing[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2019, 28(10): 2319-2330. |
| [90] |
He R W, Liu S Q, Liu Y W, et al. Application of SD model in analyzing the cultivated land carrying capacity:A case study in Bijie Prefecture, Guizho Province, China[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2011, 10: 1985-1991. DOI:10.1016/j.proenv.2011.09.311 |
| [91] |
Shi Y, Shi S, Wang H, et al. Reconsideration of the methodology for estimation of land population carrying capacity in Shanghai metropolis[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 652: 367-381. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.210 |
| [92] |
王雄.甘谷县土地资源承载力及其动态变化研究[D].兰州: 兰州大学, 2015: 11-12. WANG Xiong.Land carrying capacity and its dynamic change of Gangu County[D].Lanzhou University, 2015: 11-12. |
| [93] |
丁丹青.靖安县土地资源承载力评价研究[D].南昌: 江西农业大学, 2017: 21-47. DING Dan-qing.Evaluation of land resources carrying capacity in Jing'an County[D].Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2017: 21-47. |
| [94] |
宋先坤.康保县土地资源承载力研究[D].北京: 首都师范大学, 2009: 26-37. SONG Xian-kun.Study on the bearing capacity of land resources in Kangbao County[D].Beijing: Capital Normal University, 2009: 26-37. |
| [95] |
侯西勇, 孙希华. 耕地粮食生产潜力及人口承载力研究——以长清县为例[J]. 地球信息科学, 2002(4): 24-29. HOU Xi-yong, SUN Xi-hua. Study on cultivated land potential grain productivity and population carrying capacity[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2002(4): 24-29. |
| [96] |
高胜蓝.福建省县域耕地承载力和压力空间格局评价[D].福州: 福建农林大学, 2014: 6-7. GAO Sheng-lan.Evaluation on the spatial pattern of cultivated land carrying capacity and pressure at county level in Fujian Province[D].Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2014: 6-7. |
| [97] |
满苏尔, 阿布拉江, 艾尼瓦尔. 新疆库车县耕地人口承载能力研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2002(3): 28-32. Mansur, Abula R, Ainevar. Population bearing capacity of land in Kuqa County of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2002(3): 28-32. |
| [98] |
李团胜, 张艳, 闫颖, 等. 基于农用地分等成果的陕西周至县耕地粮食生产能力测算[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(15): 193-198. LI tuan -sheng, ZHANG Yan, YAN Ying, et al. Calculation of farmland grain potential productivity of Zhouzhi County based on agricultural land classification[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(15): 193-198. |
| [99] |
冷疏影, 李秀彬. 土地质量指标体系国际研究的新进展[J]. 地理学报, 1999(2): 3-5. LENG Shu-ying, LI Xiu-bin. New progress of international research on land quality index system[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1999(2): 3-5. |
| [100] |
戴文举, 王东杰, 卢瑛, 等. 华南地区县域耕地质量和产能评价研究——以广东吴川为例[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2019, 36(4): 419-430. DAI Wen-ju, WANG Dong-jie, LU Ying, et al. Evaluation of county level cultivated land quality and productivity in South China:A case study of Wuchuan City, Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2019, 36(4): 419-430. |
| [101] |
赵小娟.珠江三角洲地区不同尺度耕地质量评价与空间布局[D].广州: 华南农业大学, 2017: 56-126. ZHAO Xiao-juan.Quality evaluation and spatial distribution of cultivated land at different scales in the Pearl River Delta[D].Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2017: 56-126. |
| [102] |
路婕, 李玲, 吴克宁, 等. 基于农用地分等和土壤环境质量评价的耕地综合质量评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(2): 323-329. LU Jie, LI Ling, WU Ke-ning, et al. Cultivated land comprehensive quality evaluation based on agricultural land classification and soil environmental quality evaluation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 27(2): 323-329. |
| [103] |
马建辉, 吴克宁, 赵华甫, 等. 基于农用地分等的耕地质量动态监测体系研究[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2013, 34(5): 133-139. MA Jian-hui, WU Ke-ning, ZHAO Hua-fu, et al. Research on the dynamic cultivated land quality monitoring system based on the agricultural land gradation[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2013, 34(5): 133-139. |
| [104] |
彭磊, 胡月明, 吴茗华, 等. 基于农用地分等成果的耕地质量监测分区研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 2013, 40(10): 211-214, 238. PENG Lei, HU Yue-ming, WU Ming-hua, et al. Partition of cultivated land quality monitoring based on the results of agricultural land classification[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 40(10): 211-214, 238. |
| [105] |
Acton D F, Gregorich L J. The health of our soils:toward sustainable agriculture in Canada[M]. Ottawa: Centre for Land and Biological Resources Research, 1995: 70-75.
|
| [106] |
Bindraban P S, Stoorvogel J J, Jansen D M, et al. Land quality indicators for sustainable land management:Proposed method for yield gap and soil nutrient balance[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2000, 81(2): 103-112. |
| [107] |
German R N, Thompson C E, Benton T G. Relationships among multiple aspects of agriculture's environmental impact and productivity:A meta-analysis to guide sustainable agriculture[J]. Biological Reviews, 2017, 92(2): 716-738. DOI:10.1111/brv.12251 |
| [108] |
Sparling G, Schipper L. Soil quality monitoring in New Zealand:Trends and issues arising from a broad-scale survey[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2004, 104(3): 545-552. |
| [109] |
吴月良. 土地资源承载力及影响因素理论初探[J]. 农业技术经济, 1991(2): 55-61. WU Yue-liang. A preliminary study on the theory of land resources carrying capacity and influencing factors[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 1991(2): 55-61. |
| [110] |
顾芗.南京市土地开发阈值测算与土地利用结构优化[D].南京: 南京大学, 2011: 13-15. GU Xiang.Estimation of land development threshold and optimization of land use structure in Nanjing[D].Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2011: 13-15. |
| [111] |
张晓青, 李玉江. 山东省水土资源承载力空间结构研究[J]. 资源科学, 2006(2): 13-21. ZHANG Xiao-qing, LI Yu-jiang. Spatial structure of water and land resources carrying capacity in Shandong Province[J]. Resources Science, 2006(2): 13-21. |
| [112] |
赵军凯, 李九发, 戴志军, 等. 基于熵模型的城市水资源承载力研究——以开封市为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2009, 24(11): 1944-1951. ZHAO Jun-kai, LI Jiu-fa, DAI Zhi-jun, et al. Study on water resources carrying capacity of urbanized area based on entropy model:A case study in Kaifeng City[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2009, 24(11): 1944-1951. |
| [113] |
孔越, 陈娟. 社区卫生服务满意度指标体系中专家咨询法的可靠性分析[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志, 2007, 25(4): 259-261. KONG Yue, CHEN Juan. Reliability analysis of Deiphi method in the customer satisfaction index system of the community health service[J]. Journal of Preventive Medicine of Chinese People's Liberation Army, 2007, 25(4): 259-261. |
| [114] |
曹可, 张志峰, 马红伟, 等. 基于海洋功能区划的海域开发利用承载力评价——以津冀海域为例[J]. 地理科学进展, 2017, 36(3): 320-326. CAO Ke, ZHANG Zhi-feng, MA Hong-wei, et al. Capacity for resource exploitation based on marine functional zones:A case study in the Tianjin-Hebei coastal area[J]. Progress in Geography, 2017, 36(3): 320-326. |
| [115] |
徐建华. 现代地理学中的数学方法[M]. 二版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2001: 30-35. XU Jian-hua. Mathematical methods in modern geography[M]. 2nd edition. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2001: 30-35. |
| [116] |
李强, 刘剑锋, 李小波, 等. 京津冀土地承载力空间分异特征及协同提升机制研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2016, 32(1): 105-111. LI Qiang, LIU Jian-feng, LI Xiao-bo, et al. Study on spatial differentiation characteristic and collaboration enhancement mechanism of land carrying capacity in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2016, 32(1): 105-111. |
| [117] |
肖杰, 郑国璋, 郭鹏军, 等. 基于主成分分析的关中-天水经济区水资源承载力评价[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39(7): 159-167. XIAO Jie, ZHENG Guo-zhang, GUO Peng-jun, et al. Assessment of water resources carrying capacity in Guanzhong-Tianshui economic zone based on principal component analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2018, 39(7): 159-167. |
| [118] |
虞晓芬, 傅玳. 多指标综合评价方法综述[J]. 统计与决策, 2004(11): 119-121. YU Xiao-fen, FU Dai. Review of multi index comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2004(11): 119-121. |
| [119] |
李艳双, 曾珍香, 张闽, 等. 主成分分析法在多指标综合评价方法中的应用[J]. 河北工业大学学报, 1999(1): 3-5. LI Yan-shuang, ZENG Zhen-xiang, ZHANG Min, et al. Application of principal component analysis in multi index comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology, 1999(1): 3-5. |
| [120] |
林海明, 杜子芳. 主成分分析综合评价应该注意的问题[J]. 统计研究, 2013, 30(8): 25-31. LIN Hai-ming, DU Zi-fang. Some problems in comprehensive evaluation in the principal component analysis[J]. Statistical Research, 2013, 30(8): 25-31. |
| [121] |
周亮广, 梁虹. 基于主成分分析和熵的喀斯特地区水资源承载力动态变化研究——以贵阳市为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2006(5): 827-833. ZHOU Liang-guang, LIANG Hong. A study on the evolution of water resource carrying capacity in karst area based on component analysis and entropy[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2006(5): 827-833. |
| [122] |
许朗, 黄莺, 刘爱军. 基于主成分分析的江苏省水资源承载力研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2011, 20(12): 1468-1474. XU Lang, HUANG Ying, LIU Ai-jun. Study on the carrying capacity of water resources in Jiangsu Province based on the principal component analysis[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2011, 20(12): 1468-1474. |
| [123] |
李高伟, 韩美, 刘莉, 等. 基于主成分分析的郑州市水资源承载力评价[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2014, 33(3): 139-142. LI Gao-wei, HAN Mei, LIU Li, et al. Assessment of water resources carrying capacity based on principal component analysis in Zhengzhou City[J]. Areal Research and Development, 2014, 33(3): 139-142. |
| [124] |
肖迎迎, 宋孝玉, 张建龙. 基于主成分分析的榆林市水资源承载力评价[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2012, 30(4): 218-223, 235. XIAO Ying-ying, SONG Xiao-yu, ZHANG Jian-long. Assessment of water resources carrying capacity in Yulin based on principal component analysis[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2012, 30(4): 218-223, 235. |
| [125] |
Zhang F, Wang Y, Ma X J, et al. Evaluation of resources and environmental carrying capacity of 36 large cities in China based on a support-pressure coupling mechanism[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 688: 838-854. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.247 |
| [126] |
Zhu L J, Li X C, Bai Y R, et al. Evaluation of water resources carrying capacity and its obstruction factor analysis:A case study of Hubei Province, China[J]. Water, 2019, 11(12): 2573. DOI:10.3390/w11122573 |
| [127] |
鲁春阳, 文枫, 杨庆媛, 等. 基于改进TOPSIS法的城市土地利用绩效评价及障碍因子诊断——以重庆市为例[J]. 资源科学, 2011, 33(3): 535-541. LU Chun-yang, WEN Feng, YANG Qing-yuan, et al. An evaluation of urban land use performance based on the improved TOPSIS method and diagnosis of its obstacle indicators:A case study of Chongqing[J]. Resources Science, 2011, 33(3): 535-541. |
| [128] |
孙茜, 张捍卫, 张小虎. 河南省资源环境承载力测度及障碍因素诊断[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2015, 29(7): 33-38. SUN Qian, ZHANG Han-wei, ZHANG Xiao-hu. Resources and environment carrying capacity estimation and the obstacle factors diagnosis for Henan Province[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2015, 29(7): 33-38. |
| [129] |
Guang J C, Qing L. Evaluation of sustainable land management and diagnosis of obstacle at county scale in Sichuan Basin:Taking Lezhi County as example[J]. Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences, 2006, 11(4): 1046-1051. DOI:10.1007/BF02830208 |
| [130] |
卞锦宇, 黄昌硕, 耿雷华, 等. 水资源承载力诊断体系构建及关键诊断因子识别[J]. 节水灌溉, 2019(7): 56-61, 67. BIAN Jin-yu, HUANG Chang-shuo, GENG Lei-hua, et al. Diagnostic system construction of water resources carrying capacity and the key factors determination[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2019(7): 56-61, 67. |
| [131] |
侍孝瑞, 王远坤, 卞锦宇, 等. 水资源承载力关键驱动因素识别研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2018, 54(3): 628-636. SHI Xiao-rui, WANG Yuan-kun, BIAN Jin-yu, et al. Identification of key driving factors of water resources carrying capacity[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 2018, 54(3): 628-636. |
| [132] |
Si S L, You X Y, Liu H C, et al. DEMATEL Technique:A systematic review of the State-of-the-Art literature on methodologies and applications[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018(1): 1-33. |
| [133] |
任辉, 杨印生, 小池正之. 泰国的农机作业委托以及影响因素分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2001(4): 105-108. REN Hui, YANG Yin-sheng, Koike M Y. Analysis of the influencing factors on the contract hire system for agricultural machines in Thailand[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2001(4): 105-108. |
| [134] |
杨印生. 经济系统定量分析方法[M]. 长春: 吉林科学技术出版社, 2001: 169-189. YANG Yin-sheng. Quantitative analysis method of economic system[M]. Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 2001: 169-189. |
| [135] |
李银星, 杨印生. 影响我国统筹城乡发展的社会经济因素分析[J]. 农业技术经济, 2006(3): 27-31. LI Yin-xing, YANG Yin-sheng. An analysis of social and economic factors affecting the overall development of urban and rural areas in China[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2006(3): 27-31. |
| [136] |
卢秉福, 张祖立, 朱明, 等. 农业机械化发展关键影响因素的辨识与分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2008(11): 114-117. LU Bing-fu, ZHANG Zu -li, ZHU Ming, et al. Discrimination and analysis of key influencing factors for agricultural mechanization development[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2008(11): 114-117. |
| [137] |
F AO. A framework for land evaluation:FAO soils bulletin 32[M]. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 1976.
|
| [138] |
王小敏, 赵军, 王建华, 等. 基于农业生态区模型的黑河流域土地资源承载力[J]. 干旱区研究, 2014, 31(6): 991-997. WANG Xiao-min, ZHAO Jun, WANG Jian-hua. Agro-ecological assessment for land resources and carrying capacity of the Heihe River basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2014, 31(6): 991-997. |
| [139] |
Sun T, Feng Z, Yang Y, et al. Research on land resource carrying capacity:Progress and prospects[J]. Journal of Resources & Ecology, 2018, 9(4): 331-340. |
| [140] |
郭秀锐, 毛显强. 中国土地承载力计算方法研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2000(6): 705-711. GUO Xiu-rui, MAO Xian-qiang. Review of land carrying capacity calculating methods, China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2000(6): 705-711. |
| [141] |
谢俊奇, 蔡玉梅, 郑振源, 等. 基于改进的农业生态区法的中国耕地粮食生产潜力评价[J]. 中国土地科学, 2004(4): 31-37. XIE Jun-qi, CAI Yu-mei, ZHENG Zhen-yuan, et al. AEZ-based assessment for food productivity potential of cultivated land in China[J]. China Land Science, 2004(4): 31-37. |
| [142] |
蔡成凤, 刘友兆. 淮南市耕地资源生产潜力及人口承载能力研究[J]. 国土资源科技管理, 2006(2): 9-14. CAI Cheng-feng, LIU You-zhao. A study of cultivated land production potentiality and population carrying capacity of Huainan City[J]. Scientific and Technological Management of Land and Resources, 2006(2): 9-14. |
| [143] |
王连喜, 卢媛媛, 李琪, 等. 基于AEZ模型的河南省冬小麦产量差时空特征分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(4): 547-558. WANG Lian-xi, LU Yuan-yuan, LI Qi, et al. Spatio-temporal analysis of winter wheat yield gaps in Henan Province using AEZ model[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(4): 547-558. |
| [144] |
姜群鸥.基于AEZ模型的中国农业生产力的估算及其对耕地利用变化的响应[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2008: 25-39. JIANG Qun-ou.The estimation of agricultural productivity based on the AEZ model and response to the cultivated land changes[D].Changsha: Central South University, 2008: 25-39. |
| [145] |
蔡承智, Harrij V, Guenther F, 等. 基于AEZ模型的我国农区小麦生产潜力分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2007(5): 182-184. CAI Cheng-zhi, Harrij V, Guenther F, et al. Analysis of wheat production potential in agricultural areas of China based on AEZ model[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2007(5): 182-184. |
| [146] |
Wackernagel M, Onisto I, Bello P. National natural capital accounting with the the ecological footprint concept[J]. Ecological Economics, 1999, 29: 375-390. DOI:10.1016/S0921-8009(98)90063-5 |
| [147] |
张志强, 徐中民, 程国栋, 等. 中国西部12省(区市)的生态足迹[J]. 地理学报, 2001(5): 598-609. ZHANG Zhi-qiang, XU Zhong-min, CHENG Guo-dong, et al. The ecological footprints of the 12 provinces of west China in 1999[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2001(5): 598-609. |
| [148] |
刘东, 封志明, 杨艳昭. 基于生态足迹的中国生态承载力供需平衡分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2012(4): 614-624. LIU Dong, FENG Zhi-ming, YANG Yan-zhao. Ecological balance between supply and demand in China using ecological footprint method[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2012(4): 614-624. |
| [149] |
张红, 陈嘉伟, 周鹏. 基于改进生态足迹模型的海岛城市土地承载力评价——以舟山市为例[J]. 经济地理, 2016, 36(6): 155-160. ZHANG Hong, CHEN Jia-wei, ZHOU Peng. A modified ecological footprint model to evaluate the land carrying capacity of island cities:Take Zhoushan City as example[J]. Economic Geography, 2016, 36(6): 155-160. |
| [150] |
Forrester J.W. Industrial dynamics:A major breakthrough for decision makers[J]. Harvard Business Review, 1958, 36(4): 37-66. |
| [151] |
王其藩. 高级系统动力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1995: 1-20. WANG Qi-fan. Advanced system dynamics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1995: 1-20. |
| [152] |
陈国卫, 金家善, 耿俊豹. 系统动力学应用研究综述[J]. 控制工程, 2012, 19(6): 921-928. CHEN Guo -wei, JIN Jia-shan, GENG Jun-bao. Application research overview of system dynamics[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2012, 19(6): 921-928. |
| [153] |
Wei F, An H Z, Li H J, et al. Urban economy development and ecological carrying capacity:Taking Beijing City as the case[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 105: 3493-3498. DOI:10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.801 |
| [154] |
杨子江, 韩伟超, 杨恩秀. 昆明市水资源承载力系统动力学模拟[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(3): 594-602. YANG Zi-jiang, HAN Wei-chao, YANG En-xiu. A system dynamic model and simulation for water resources carrying capacity in Kunming[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2019, 28(3): 594-602. |
| [155] |
傅湘, 纪昌明. 区域水资源承载能力综合评价——主成分分析法的应用[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 1999(2): 3-5. FU Xiang, JI Chang-ming. A comprehensive evaluation of the regional water resource carrying capacity:Application of main component analysis method[J]. Resources and Enuironment in the Yangtza Basin, 1999(2): 3-5. |
| [156] |
惠泱河, 蒋晓辉, 黄强, 等. 水资源承载力评价指标体系研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2001(1): 30-34. HUI Yang-he, JIANG Xiao-hui, HUANG Qiang, et al. Research on evaluation index system of water resources bearing capacity[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2001(1): 30-34. |
| [157] |
徐永胜. 土地人口承载力问题初探[J]. 人口研究, 1991(5): 37-42. XU Yong-sheng. A preliminary study on the carrying capacity of land population[J]. Population Research, 1991(5): 37-42. |
| [158] |
Jiang Q X,Fu Q,Meng J,et al.Comprehensive evaluation of land resources carrying capacity under different scales based on RAGAPPC[C].Beijing:International Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture,2014:200-209.
|
| [159] |
滕宇思.基于系统动力学的西安市土地综合承载力评价与预测研究[D].西安:西北工业大学,2016:27-95. TENG Yu-si.Research on evaluation and prediction of land comprehensive carrying capacity in Xi'an City based on system dynamics[D].Xi'an:Northwest University of Technology,2016:27-95. |
| [160] |
卢必慧.基于多指标体系的临安市土地资源承载力综合评价研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2014:21-50. LU Bi-hui.Study on comprehensive carrying capacity of land resources in Lin'an based on multi-index system[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2014:21-50. |
| [161] |
Adnane M, Ewa B A. New tool for assessing urban water carrying capacity(WCC)in the planning of development programs in the region of Oran,Algeria[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2019, 48: 101316. DOI:10.1016/j.scs.2018.10.040 |
| [162] |
王书华, 毛汉英. 土地综合承载力指标体系设计及评价——中国东部沿海地区案例研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2001, 16(3): 248-254. WANG Shu-hua, MAO Han-ying. Design and evaluation on the indicator system of land comprehensive carrying capacity[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2001, 16(3): 248-254. |
| [163] |
Ferreira J G, Hawkins A J S, Hawkins P X, et al. Integrated assessment of ecosystem-scale carrying capacity in shellfish growing areas[J]. Aquaculture, 2008, 275(1/2/3/4): 138-151. |
| [164] |
Wu X L, Hu F. Analysis of ecological carrying capacity using a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 113: 106243. DOI:10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106243 |
| [165] |
Wu L, Su X L, Ma X Y, et al. Integrated modeling framework for evaluating and predicting the water resources carrying capacity in a continental river basin of northwest China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 204: 366-379. DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.319 |
| [166] |
祝秀芝, 李宪文, 贾克敬, 等. 上海市土地综合承载力的系统动力学研究[J]. 中国土地科学, 2014, 28(2): 90-96. ZHU Xiu-zhi, LI Xian-wen, JIA ke-jing, et al. A study on system dynamics of land comprehensive carrying capacity in Shanghai City[J]. China Land Sciences, 2014, 28(2): 90-96. |
| [167] |
周力.做好外部环境恶化的六大准备[N].中华工商时报,2020-08-14(3). ZHOU Li.Six preparations for deterioration of external environment[N].China Business Times,2020-08-14(3). |
 2020, Vol. 37
2020, Vol. 37