2. 新疆农业科学院经济作物研究所, 乌鲁木齐 830091;
3. 中国农业科学院农业环境与可持续发展研究所, 北京 100081
2. Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences Cash Crop Research Institute, Urumqi 830091, China;
3. Institute of Agriculture Environment and Sustainable Development, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 100081, China
地膜覆盖具有增温保墒、控盐抑碱和增产等作用,已成为重要的农业增产技术措施,在新疆地区被广泛应用[1-6]。目前,新疆是全国最大的地膜覆盖种植区,覆盖率达到100%,膜下滴灌棉花面积超过200万hm2[7]。40年地膜的大面积应用使土壤中残留大量残膜,降低土壤通气透水性,造成缺苗断垄等,阻碍农业可持续发展[8]。新疆棉区土壤残膜污染最为严重,耕层平均残膜量为265.3 kg·hm-2,是全国平均水平的4.5倍,最高达381.1 kg·hm-2 [9-11]。解决残膜问题刻不容缓,而可降解地膜具有自然条件下可降解的优点[12-16],成为解决残膜污染的理想途径[12]。目前国内外已研发出不同类型的可降解地膜,如光降解地膜、生物降解地膜、光-生物双降解地膜、多功能可降解液态地膜[17-19]等。赵岩等[19]认为目前可降解地膜和普通地膜会长期共存,降解地膜对棉花的生长发育、成铃及产量[20]有一定促进作用。由于作物种类和应用区域气候条件等有差异,与普通地膜相比,降解膜覆盖作物的产量高低不一[21-22]。在新疆北部棉区,有研究对覆盖降解地膜的棉花生长及产量进行了分析[23-24],而南疆棉田覆盖可降解地膜的研究并不多,朱友娟等[25]研究表明,覆盖可降解地膜与普通地膜相比,棉花衣分、单铃质量、籽棉产量等指标无显著差异。本试验研究南疆棉田覆盖可降解膜对棉花生长及产量等影响,确定适宜新疆南部棉区的可降解膜,为可降解膜的选用和降低残膜污染提供依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验地概况田间试验于2017年4—10月在新疆阿克苏市新疆农业科学院阿瓦提棉花综合实验站进行。试验地属于典型的暖温带大陆性干旱气候,年日照时数为2750~3029 h,太阳总辐射量为5340~6220 MJ·m-2,无霜期183~227 d,年平均气温9.9~11.5 ℃,全年≥10 ℃积温3 802.9 ℃,年降水量42.4~94.4 mm,在时间上分布不均,蒸发量大,寒暑变化剧烈,试验区耕作层(0~40 cm)土壤为砂壤土。
1.2 试验材料试验用三种氧化-生物双降解生态地膜(天壮1号、天壮2号、天壮3号,山东天壮环保科技有限公司生产)和一种生物分解地膜(华盛),地膜幅宽均为205 cm,厚度均为0.01 mm。供试棉花品种为新陆中54号。
1.3 试验方法试验设置5个处理,分别是地膜天壮1号(T1)、天壮2号(T2)、天壮3号(T3)、华盛(HS)和普通地膜(PE),小区试验随机区组排列,小区面积为46.8 m2,总面积702 m2,试验设重复3次。4月19日播种,同时覆膜,本试验采用一膜六行(66 cm+10 cm)宽窄行相间的种植模式,株距为10 cm,田间理论密度为27.7万株·hm-2,棉田的日常管理同一般大田。
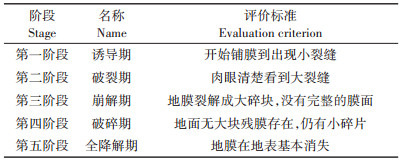
1.4 测定项目与方法降解膜的降解性能:采用何文清等[26]降解评价目测法,定期记录地膜形态以及表面完整性的变化情况,评价田间覆盖试验降解强度。地面暴露部分的降解过程分为5个阶段,具体评价标准见表 1。
|
|
表 1 降解膜田间降解观测标准 Table 1 The standard of degradable mulch in the field |
农艺性状的调查:在每个试验小区选取第二膜长势均匀的10株棉株挂牌定株,内外行各5株。在棉花不同生育时期(苗期、蕾期、花期、铃期、吐絮期)调查株高、果枝数、蕾数、铃数等性状指标。
干物质的测定:在试验田内选择长势均匀具有代表性的区域设置取样小区。在棉花苗期、蕾期、盛花期、盛铃期、吐絮期选择长势均匀具有代表性植株6株(取边行3株、中行3株),将其分解成叶、茎、蕾、铃花、根,105 ℃杀青30 min,80 ℃烘干至恒质量,称干质量。对边行和中行的干质量求其均值。
产量的测定:在棉花吐絮期,在每小区组内棉株的上、中、下部各选取50朵棉花,称量其籽棉质量,轧花后称其皮棉质量,通过计算获取单铃质量和衣分等指标。
1.5 数据处理与分析采用Excel 2013和DPS 7.05进行数据处理及分析,方差分析均为α=0.05水平,采用LSD法。
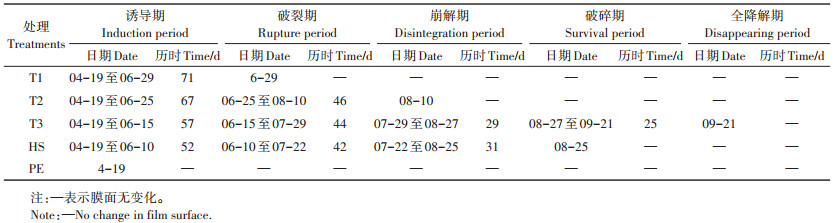
2 结果与分析 2.1 不同地膜的田间降解速度本试验降解地膜诱导期为39~71 d,可降解膜降解速率均不同(表 2)。HS膜面最快出现缝隙,诱导期为52 d,比T1、T2、T3缩短19、15、5 d。T3在播种155 d后进入全降解期,接近粉末状,小碎块数量明显减少。T1在播种71 d后进入破裂期,膜面出现肉眼可见的大缝隙。T2在播种113 d后进入崩解期,膜面出现肉眼可见的大碎块。HS在播种125 d后进入破碎期,膜面裂解为小碎块,HS前期降解快,而后期慢。普通地膜全程膜面没有变化。可得出T3降解速率最快,其次是HS,T2、T1降解较慢。
|
|
表 2 不同地膜表观目测降解时间进程 Table 2 Apparent visual degradation time of different mulching films |
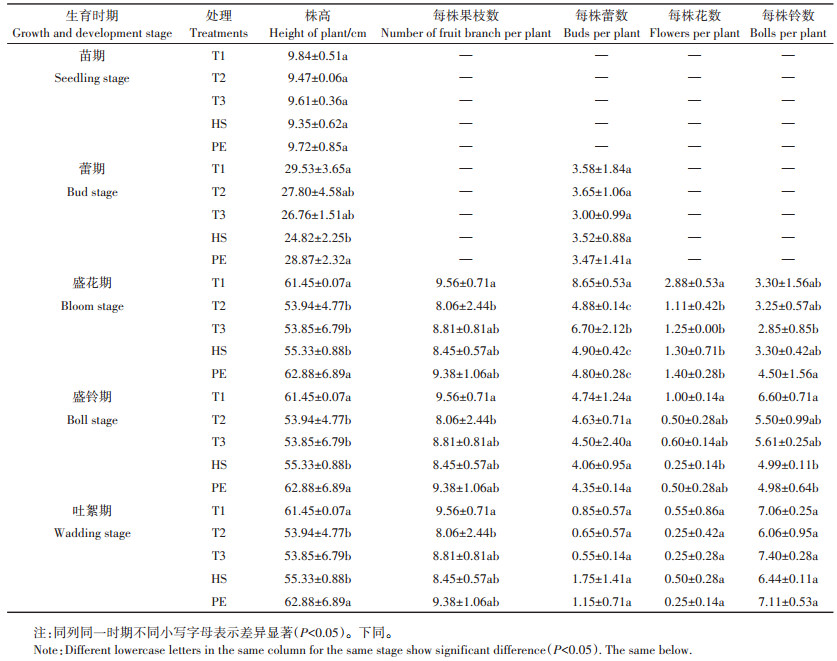
在关键生育时期进行棉花农艺性状测定,结果(表 3)表明,苗期棉花株高各处理无显著差异;在蕾期时,PE、T1株高比T2、T3、HS高;其他生育时期T1与PE株高无差异,但均显著高于其他处理。果枝数在各时期均为T1处理显著高于T2处理18.61%,其他各处理间无显著差异。盛花期蕾数,PE比T1、T3显著减少44.51%、28.36%,而其他生育时期蕾数各处理间均无显著差异。盛花期花数,T1显著高于其他处理,其他处理间无显著差异;盛铃期花数,HS显著低于T1处理75.00%,其他处理间无显著差异。盛铃期铃数,PE比T1显著减少24.54%;吐絮期铃数,各处理间无显著差异。综上可得,至吐絮期时,PE、T1株高显著高于其他处理,果枝数、蕾数、花数、铃数与其他处理无显著差异;T2、T3花数、铃数在各生育时期差异均不明显;HS蕾数和花数在吐絮期之前较低,而吐絮期时与其他处理无明显差异,可见HS处理棉花生长进程缓慢。
|
|
表 3 不同地膜对棉花农艺性状的影响 Table 3 Effects of different plastic mulching on the agronomic traits of cotton |
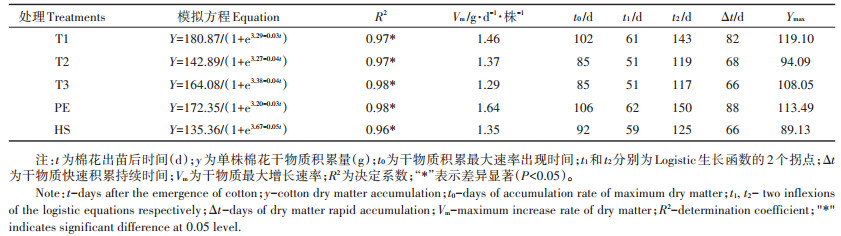
覆盖不同地膜的棉花干物质积累呈Logistics生长曲线(表 4),呈现缓慢增长-快速增长-缓慢增长的过程。各处理出现的2个拐点时间不同,T1、PE第一拐点出现时间比T2、T3、HS晚,第二拐点时间同样也晚,从快速增长(Δt)时间来看,PE比T1、T2、T3、HS分别长6、20、22、22 d,PE速度特征值(Vm)比T1、T2、T3、HS分别高12.33%、19.71%、27.13%、19.26%。干物质积累最大量Ymax,PE比T2、T3、HS增加20.62%、5.03%、27.33%,比T1减少4.71%。干物质积累最大时刻t0,T2、T3在出苗后85 d达到干物质最大积累速率,比T1、PE分别早17、21 d。综上可得,T2、T3、HS干物质积累开始时间早、最大累积速率低、快速累积期持续时间短,PE和T1棉花快速增长期时间较长,干物质总积累量较大。
|
|
表 4 不同地膜处理总干物质积累模型方程 Table 4 Model equation for the accumulation of total dry matter in different mulching film |
不同地膜覆盖的棉花产量见表 5。由表 5可知, 普通地膜单株结铃数比T1、T2、T3、HS高19.30%、38.78%、36.00%、54.55%,单株结铃数依次为PE>T1> T3>T2>HS。普通地膜衣分与其他处理无显著差异。与普通地膜相比,HS籽棉产量显著减少30.26%。T1比普通地膜单株结铃数少,但籽棉产量最高,说明T1具有增产效果;T2单株铃数较少,但单铃质量最高,籽棉产量与普通地膜差异不显著;HS达不到普通地膜的籽棉产量;T3籽棉产量与普通地膜差异不大,与HS差异显著。
|
|
表 5 不同地膜的产量及产量构成因子 Table 5 Yield and yield components of different mulching films |
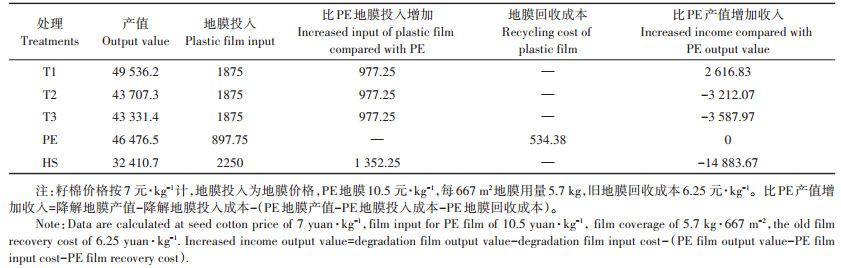
不同地膜覆盖的棉花经济效益有差异(表 6)。各处理棉花产值从高到底依次为T1>PE>T2>T3>HS。与普通地膜收入产值相比,T2、T3、HS分别减收7.13%、7.97%、33.04%,而T1增收5.81%。
|
|
表 6 不同地膜处理投入及产出分析比较(元·hm-2) Table 6 Analysis and comparison of input and output of different plastic film treatments(yuan·hm-2) |
本试验T1、T2、T3为氧化-生物双降解地膜,HS为生物降解地膜,降解情况差异显著,HS在播种125 d后膜面裂解为小碎块,降解速率快。生物可降解地膜主要成分为聚己二酸丁二醇酯-对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯(PBAT),苯二甲酸丁二醇(PET)具有稳定性,降解速率低[27]。本试验生物降解膜HS降解速率表现相反,可能与当地气候类型、光照、土壤质地及种植方式有关。温度越高、水分越大,生物降解地膜降解越强烈[28],例如,河北年均气温高,降雨量多,生物降解膜降解迅速[26, 29]。因此,加强降解地膜的稳定性与可控性,除了化学成分,还需考虑不同的气候环境。
可降解膜诱导期的长短影响降解速率。本试验供试降解膜诱导期为39~71 d,T1诱导期为71 d,降解速率最慢;T3诱导期为57 d,播种155 d后地膜基本消失,降解速率最快;HS、T2诱导期分别为52、67 d。南殿杰等[30]认为,棉花上覆盖可降解地膜,其诱导期控制在60 d左右为宜,本试验T2、T3、HS符合该条件。周明冬等[31]研究表明,降解地膜的降解速度对棉花生长发育及产量的影响较大,主要体现在降解膜的不同裂解时段,可知诱导期是重要因素之一。严昌荣等[32]提出的“作物地膜覆盖安全期”,为降解地膜确定诱导期天数提供了思路,可以此来确定诱导期天数,控制降解速度,达到满足作物生长发育最佳天数后自然降解。
3.2 可降解膜的降解速率对棉花生长及产量的影响降解地膜降解速率的快慢对棉株生长发育及产量有较大影响。周明冬等[31]认为,降解性能是影响作物生长期增温保墒效果的直接因素,是作物生长和产量的间接因素,降解速率越快,增温保墒效果越差,不利于作物生长,造成减产。与普通地膜相比,本试验中T1降解速率慢,促进棉花生长和干物质积累,增加籽棉产量;而HS前期降解过早,对棉花生长发育不利,降低光合物质的积累,减产达30.26%;T2、T3产量差异不明显。王宁等[33]认为,厚度为0.012 mm的降解膜提高棉花产量的生物学效应与普通地膜相似,这与本试验厚度为0.01 mm的T1结果相似;何文清等[26]研究表明降解膜降解速度过快,造成显著的减产,这与本文HS结果相似;朱友娟等[25]研究认为可降解地膜与普通地膜相比,对棉花的生长及产量无显著优势,这与本试验T2、T3表现一致。不同地区、不同作物覆盖相应降解速率的降解膜,既利于作物生长,又能解决残膜污染问题。
4 结论(1)在干旱少雨、蒸发量大、砂壤土的新疆南部棉区,T1、T2、T3、HS地膜诱导期分别为71、67、57、52 d。T1产值较普通地膜增收5.81%,HS减收33.04%,T2、T3分别减收7.13%、7.97%。
(2)综合经济效益与生态效益,T3降解地膜较适宜南疆棉田,其在4月中旬铺膜后57 d进入破裂期,101 d后进入崩解期,130 d后进入破碎期,155 d后进入全降解期。
| [1] |
严昌荣, 刘恩科, 舒帆, 等. 我国地膜覆盖和残留污染特点与防控技术[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(2): 95-102. YAN Chang-rong, LIU En-ke, SHU Fan, et al. Review of agricultural plastic mulching and its residual pollution and prevention measures in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(2): 95-102. |
| [2] |
冯迪, 郝庆菊, 张凯莉, 等. 地膜覆盖对菜地生态系统N2O排放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(10): 4380-4389. FENG Di, HAO Qing-ju, ZHANG Kai-li, et al. Effects of plastic film mulching on nitrous oxide emissions from a vegetable field[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(10): 4380-4389. |
| [3] |
王友贞, 袁先江, 许浒, 等. 水稻旱作覆膜的增温保墒效果及其对生育性状影响研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2002, 18(2): 29-31. WANG You-zhen, YUAN Xian-jiang, XU Hu, et al. Effects of plastic film mulching on temperature increase and preservation of soil moisture and its responses to growth character of rice with dry-land cultivation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2002, 18(2): 29-31. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2002.02.008 |
| [4] |
买自珍, 程炳文, 王勇, 等. 麦草与地膜覆盖对玉米田间生态环境及产量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2007, 15(2): 66-68. MAI Zi-zhen, CHENG Bing-wen, WANG Yong, et al. Effects of plastic film and straw mulching on field environment and yield of maize[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2007, 15(2): 66-68. |
| [5] |
Chen Y L, Liu T, Tian X H, et al. Effects of plastic film combined with straw mulch on grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in Loess Plateau[J]. Field Crops Research, 2015, 172: 53-58. DOI:10.1016/j.fcr.2014.11.016 |
| [6] |
Jiang L, Dami I E, Doohan D J, et al. Effects of mulching on soil temperature, scion rooting, and soil moisture of mounded grapevines[J]. International Journal of Fruit Science, 2016, 16(2): 182-190. DOI:10.1080/15538362.2015.1105170 |
| [7] |
王振华, 杨培岭, 郑旭荣, 等. 新疆现行灌溉制度下膜下滴灌棉田土壤盐分分布变化[J]. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45(8): 149-159. WANG Zhen-hua, YANG Pei-ling, ZHENG Xu-rong, et al. Soil salt dynamics in cotton fields with mulched drip irrigation under the existing irrigation system in Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(8): 149-159. |
| [8] |
解红娥, 李永山, 杨淑巧, 等. 农田残膜对土壤环境及作物生长发育的影响研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007(S1): 153-156. XIE Hong-e, LI Yong-shan, YANG Shu-qiao, et al. Influence of residual plastic film on soil structure, crop growth and development in fields[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007(S1): 153-156. |
| [9] |
朱会义. 1980年以来中国棉花生产向新疆集中的主要原因[J]. 地理研究, 2013, 32(4): 744-754. ZHU Hui-yi. The main reason why cotton production in China has concentrated in Xinjiang since 1980[J]. Geographical Research, 2013, 32(4): 744-754. |
| [10] |
国家统计局农村社会调查总队. 新中国五十年农业统计资料[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2000. Headquarters of Rural Social Survey of the State Statistical Bureau. Agricultural statistics of New China for fifty years[M]. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House, 2000. |
| [11] |
严昌荣, 王序俭, 何文清, 等. 新疆石河子地区棉田土壤中地膜残留研究[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(7): 3470-3484. YAN Chang-rong, WANG Xu-jian, HE Wen-qing, et al. The residue of plastic film in cotton fields in Shihezi, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(7): 3470-3484. |
| [12] |
黎先发. 可降解地膜材料研究现状与进展[J]. 塑料, 2004(1): 76-81. LI Xian -fa. Study status on degradable mulching film[J]. Plastics, 2004(1): 76-81. |
| [13] |
李强, 王琦, 张恩和, 等. 生物可降解地膜覆盖对干旱灌区玉米产量和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(9): 155-159. LI Qiang, WANG Qi, ZHANG En-he, et al. Effects of biodegradable film mulching on grain yields and water use efficiency of maize in arid oasis irrigation area[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(9): 155-159. |
| [14] |
王淑英, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 等. 生物降解膜降解、保墒增温性能及对玉米生长发育进程的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2016, 34(1): 127-133. WANG Shu-ying, FAN Ting-lu, LI Shang-zhong, et al. Property of biodegradable film degradation, water retention and increasing soil temperature and its impact on maize growth and development process[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2016, 34(1): 127-133. |
| [15] |
康虎, 敖李龙, 秦丽珍, 等. 生物质可降解地膜的田间降解过程及其对玉米生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(6): 54-58. KANG Hu, AO Li-long, QIN Li-zhen, et al. Effects of biodegradable mulch film by reusing biomass residue on degradation in field and corn growth[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(6): 54-58. |
| [16] |
李丽霞, 陈海涛. 可降解地膜原料大豆秸秆纤维的制备工艺及参数优化[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(13): 269-275. LI Li-xia, CHEN Hai-tao. Preparation technology and parameters optimization for soybean straw fiber as biodegradable film material[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(13): 269-275. |
| [17] |
Li C, Moore-Kucera J, Lee J, et al. Effects of biodegradable mulch on soil quality[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2014, 79: 59-69. DOI:10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.02.012 |
| [18] |
Briassoulis D, Dejean C. Critical review of norms and standards for biodegradable agricultural plastics part Ⅰ. Biodegradation in soil[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 2010, 18(3): 384-400. DOI:10.1007/s10924-010-0168-1 |
| [19] |
赵岩, 陈学庚, 温浩军, 等. 农田残膜污染治理技术研究现状与展望[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(6): 1-14. ZHAO Yan, CHEN Xue-geng, WEN Hao-jun, et al. Research status and prospect of control technology for residual plastic film pollution in farmland[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(6): 1-14. |
| [20] |
关新元, 尹飞虎, 刘齐锋, 等. 降解地膜在棉花上应用效果初探[J]. 新疆农垦科技, 2001(4): 37-38. GUAN Xin-yuan, YIN Fei-hu, LIU Qi-feng, et al. Preliminary study on the application effect of degradable plastic film on cotton[J]. Xinjiang Farm Research of Science and Technology, 2001(4): 37-38. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-361X.2001.04.017 |
| [21] |
张杰, 任小龙, 罗诗峰, 等. 环保地膜覆盖对土壤水分及玉米产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(6): 14-19. ZHANG Jie, REN Xiao-long, LUO Shi-feng, et al. Influences of different covering materials mulching on soil moisture and corn yield[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2010, 26(6): 14-19. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2010.06.003 |
| [22] |
戴敬, 陈荣来, 李国军. 可降解地膜覆盖棉花增产效应的研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2004, 12(2): 145-147. DAI Jing, CHEN Rong-lai, LI Guo-jun. The increasing yield effects of degradable plastic film mulching on the cottons[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2004, 12(2): 145-147. |
| [23] |
董学礼, 陈福, 杨素梅. 降解膜降解效果试验初报[J]. 宁夏农业科技, 1999(4): 45-46. DONG Xue-li, CHEN Fu, YANG Su-mei. Preliminary report on degradation effect of degradable membrane[J]. Ningxia Agricultural Science and Technology, 1999(4): 45-46. |
| [24] |
胡伟, 孙九胜, 单娜娜, 等. 降解地膜对地温和作物产量的影响及其降解性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2015, 52(2): 317-320. HU Wei, SUN Jiu-sheng, SHAN Na-na, et al. Effect of COPO degradable membrane on soil temperature and crop yield and analysis of its degradable characteristics[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 52(2): 317-320. |
| [25] |
朱友娟, 伍维模, 温善菊, 等. 可降解地膜对新疆南疆棉花生长和产量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2016, 34(4): 189-196, 224. ZHU You-juan, WU Wei-mo, WEN Shan-ju, et al. The effect of degradable agricultural mulch films on the growth and yield of cotton in southern Xinjiang[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2016, 34(4): 189-196, 224. |
| [26] |
何文清, 赵彩霞, 刘爽, 等. 全生物降解膜田间降解特征及其对棉花产量影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2011, 16(3): 21-27. HE Wen-qing, ZHAO Cai-xia, LIU Shuang, et al. Study on the degradation of biodegradable plastic mulch film and its effect on the yield of cotton[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2011, 16(3): 21-27. |
| [27] |
邬强, 王振华, 郑旭荣, 等. PBAT生物降解膜覆盖对绿洲滴灌棉花土壤水热及产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(16): 135-143. WU Qiang, WANG Zhen-hua, ZHENG Xu-rong, et al. Effects of biodegradation film mulching on soil temperature, moisture and yield of cotton under drip irrigation in typical oasis area[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(16): 135-143. DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.16.018 |
| [28] |
乔海军, 黄高宝, 冯福学, 等. 生物全降解地膜的降解过程及其对玉米生长的影响[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2008(5): 71-75. QIAO Hai-jun, HUANG Gao-bao, FENG Fu-xue, et al. Degradation and its effect on corn growth of biodegradable mulch film[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2008(5): 71-75. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-4315.2008.05.015 |
| [29] |
王鑫, 胥国斌, 任志刚, 等. 无公害可降解地膜对玉米生长及土壤环境的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2007, 15(1): 78-81. WANG Xin, XU Guo-bin, REN Zhi-gang, et al. Effects of environment-friendly degradable films on corn growth and soil environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2007, 15(1): 78-81. |
| [30] |
南殿杰, 解红娥, 李燕娥, 等. 覆盖光降解地膜对土壤污染及棉花生育影响的研究[J]. 棉花学报, 1994, 6(2): 103-108. NAN Dian-jie, XIE Hong-e, LI Yan-e, et al. Study of the effect of photodegradable plastic film mulching on soil contamination and cotton growth[J]. Cotton Science, 1994, 6(2): 103-108. |
| [31] |
周明冬, 秦晓辉, 韩咏香. 降解膜对棉花生长及产量的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, 2014(4): 17, 19. ZHOU Ming-dong, QIN Xiao-hui, HAN Yong-xiang. Effects of degradable film on cotton growth and yield[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2014(4): 17, 19. |
| [32] |
严昌荣, 何文清, 刘恩科, 等. 作物地膜覆盖安全期概念和估算方法探讨[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(9): 1-4. YAN Chang-rong, HE Wen-qing, LIU En-ke, et al. Concept and estimation of crop safety period of plastic film mulching[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(9): 1-4. |
| [33] |
王宁, 冯克云, 南宏宇, 等. 生物降解膜对甘肃河西棉花的生态生物学效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(11): 3607-3614. WANG Ning, FENG Ke-yun, NAN Hong-yu, et al. Ecological and biological effects of biodegradable film on cotton in Hexi area of Gansu, northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(11): 3607-3614. |
 2019, Vol. 36
2019, Vol. 36