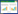文章信息
- 渠清博, 杨鹏, 翟中葳, 张克强
- QU Qing-bo, YANG Peng, ZHAI Zhong-wei, ZHANG Ke-qiang
- 规模化畜禽养殖粪便主要污染物产生量预测方法研究进展
- Prediction Methods of Major Pollutants Production in Manure from Large-scale Livestock and Poultry Farms: A Review
- 农业资源与环境学报, 2016, 33(5): 397-406
- Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2016, 33(5): 397-406
- http://dx.doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2016.0046
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2016-02-21
规模化畜禽养殖业的快速发展集中产生了大量的畜禽粪便,这些粪便中富含有机质、氮、磷等主要污染物,若得不到及时有效的处理和利用,将会对环境造成严重的污染。为了有效地预防和控制畜禽粪便对环境的污染,实现其资源化和无害化利用,合理估算和预测畜禽粪便主要污染物的产生量和浓度是非常必要的。
产污系数作为畜禽养殖业污染状况的重要基础数据,是对畜禽粪便主要污染物含量平均水平的估算值,其主要分为两大类:全国或大区产污系数[1-5]及分省或分地区产污系数[6-13]。该系数对区域畜禽养殖产排污量的快速核算[14]、宏观层面上了解畜禽粪便污染状况[15-16]以及相关政策的制定具有重要的意义。此外,数学模型法作为一种定量预测方法,其在畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量预测方面的应用也越来越普遍。如Tomlinson等[17],Nennich等[18],Higgs等[19],杨增玲等[20],Dragun[21],Moral等[22],Suresh等[23],韩鲁佳等[24],Reeves[25],Saey等[26]分别从不同的角度出发,建立了基于畜禽日粮营养成分、粪便理化指标以及近红外光谱分析等快速预测畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量的经验模型。这些经验模型为畜禽养殖场快速估算、预测畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量、实现畜禽粪便合理的资源化和无害化提供了科学依据。
但目前的研究缺乏对2种预测方法的系统总结,对其特点及适用范围也不够明确。因此本文通过综述近几年国内外关于畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量预测方法的研究进展,分别对产污系数法和数学模型法进行了归纳,重点讨论了各预测方法的预测精度、主要特点及适用范围,并对其进一步的研究方向进行了展望,旨在为合理应用预测方法,正确估算畜禽养殖粪便主要污染物产生量提供参考。
1 产污系数法产污系数法是指在典型的正常生产和管理条件下,利用某一固定系数对单位畜禽原始粪便日/年主要污染物产生量的平均水平进行估算。其主要分为两大类:一类是全国或大区一致的固定系数,另一类为分省产污系数,即以统一系数为基础,结合实测与经验进行修正。
1.1 全国或大区产污系数全国或大区产污系数主要反映全国或大区不同畜禽种类粪尿日/年主要污染物产生量的平均水平,可为宏观了解畜禽养殖业的产污状况提供参考。随着畜禽养殖业环境污染问题的突出,世界各国纷纷根据本国畜禽养殖的特点制定了相应的产污系数。如日本《畜产环境对策大事典》在畜禽粪尿特性和产污系数方面提供了大量的参考数据[1]。丹麦农业科学研究所也出版有主要畜禽粪尿氮、磷产污系数[2]。美国农业工程师协会(ASAE)2005年编制出版的《动物粪便产生和特性参数》对典型日粮条件下,不同畜禽粪尿主要污染物产生量进行了估算,即产污系数[3]。我国相关部门和研究机构也相继发布了畜禽养殖业产污系数,如2002年编写的《全国规模化畜禽养殖业污染情况调查及防治对策》,对主要畜种(牛、猪、羊、鸡、鸭)粪尿日/年主要污染物的排泄系数(即产污系数)进行了估算[4]。之后2007年第一次全国污染源普查,进一步对不同区域、不同养殖阶段畜禽粪尿主要污染物产生量进行了估算,形成了以华北、东北、华东、中南、西南、西北6大区、不同养殖阶段、5个畜种为主要对象的畜禽粪尿化学需氧量、氮、磷及铜、锌产生系数的《第一次全国污染源普查畜禽养殖业产排污系数手册》[5]。该系数使全国尺度下畜禽污染物产排量估算结果的精度进一步提升。
不同国家主要畜禽粪便产污系数如表 1所示。由表 1可知,不同国家同一畜种粪便产污系数存在一定差异,丹麦畜禽粪便产污系数相对较低,美国较高,而中国畜禽粪便产污系数变化范围较大。造成这种差异的原因一方面主要与各国畜禽养殖品种、饲料组成、饲养模式以及季节气候等有关。例如,丹麦人口和资源相对稳定,养殖场规模适度,大多采用农牧结合的家庭农场经营模式,其污染物产生量相对较少,产污系数相对较低。而美国畜禽养殖业大多采用机械化的经营模式,集约化程度较高,各污染物产生量较大,产污系数的标准值相对较高。我国畜禽养殖区域化较明显,不同区域的污染物产生量差异较大[6-13]。另一方面也与各国产污系数的核算方法有关。如国外对于产污系数的提出或根据已发表的文献,对畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量的平均值进行估算;或基于相关方程,对典型日粮条件下畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量进行预测。而我国产污系数的提出则主要基于对养殖场畜禽粪便及其主要污染物产生量的监测数据,通过对监测结果的分析,得出全国或大区尺度上不同畜种粪便主要污染物产生量的平均值。
|
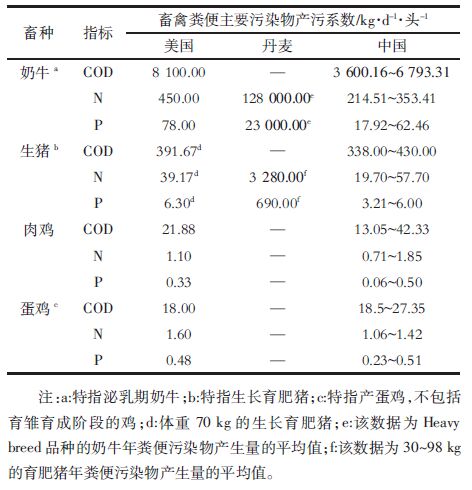
在实际应用中,由于不同省份在气候条件、养殖方式和饲料组成等方面存在差异,采用全国或大区畜禽粪便产污系数不能真实反映各省或各地区的畜禽产污量。针对这一问题,相关研究人员开展了分省或分地区畜禽粪便产污系数的研究。如董红敏等[6]、苏文幸[7]、谢飞等[8]、汪开英等[9]、何志平等[10] 分别对北京、黑龙江、海南、湖南、江苏、浙江、四川等不同地区典型规模养殖场不同生长阶段生猪粪便主要污染物产污系数进行了测定(表 2)。王会群等[11]、栾冬梅等[12]、张振伟等[13] 分别对河南、黑龙江、宁夏等不同地区规模化奶牛养殖场育成牛、泌乳牛粪尿主要污染物产污系数进行了测定(表 3)。由表 2、表 3可知,各省份畜禽产污系数与全国或大区产污系数存在较大差异,且不同省份同一生长阶段的畜种的产污系数也存在一定差别。分省或分地区产污系数的研究主要针对某一地区特定条件下的养殖场,该类系数更符合各省畜禽养殖的污染特点,实用性更强,更能真实反映各省或各地区畜禽养殖主要污染物的产生量。

|
|
数学模型法是根据全面且可靠的基础数据及实测数据,利用现代数据处理技术,找出各参量之间的函数关系建立起来的预测粪便主要污染物含量的数学模型。目前国内外预测畜禽粪便主要污染物含量的数学模型主要集中于以下3个方面:(1)基于日粮营养组成快速预测畜禽粪便主要污染物含量;(2)基于粪便理化性质快速预测畜禽粪便主要污染物含量;(3)基于近红外光谱分析快速预测畜禽粪便主要污染物含量。
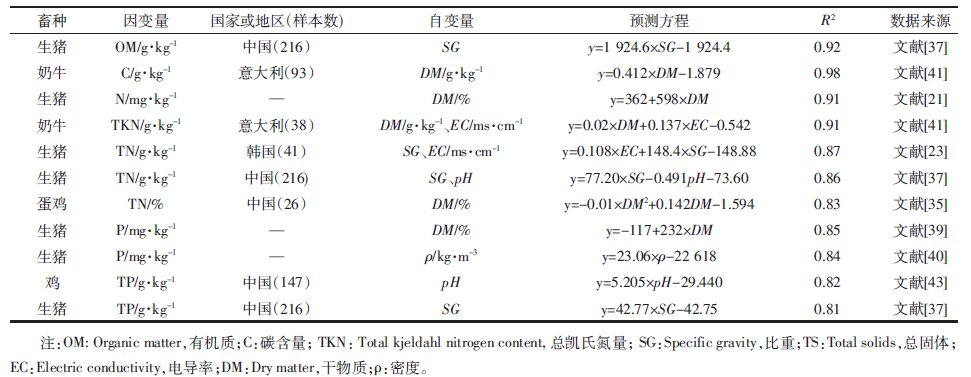
2.1 基于日粮营养组成快速预测畜禽粪便主要污染物含量研究表明畜禽粪便主要污染物的含量与动物的种类、品种、性别、生长期、体重、日粮组成及季节气候等诸多因素有关,其中日粮因素起主导作用[27-30]。许多研究人员基于理论分析和实验基础,探讨了畜禽日粮营养组成与其粪便主要污染物含量的相关性,建立了基于日粮营养组成快速预测畜禽粪便主要污染物含量的回归方程[17-19, 31-34]。如Tomlinson等[17],Nennich等[18],Higgs等[19],Yan等[31],Jiao等[32]基于日粮营养物质含量建立了多个预测奶牛粪便主要污染物含量的数学统计模型(表 4)。研究发现,奶牛体重及日粮中干物质的摄入量与奶牛粪便有机质含量线性相关性较强,基于其建立的回归方程的相关系数约在0.8左右,表明利用奶牛体重及日粮干物质摄入量可较好地预测奶牛粪便有机质含量。而奶牛粪便N、P的产生量与日粮中相应元素的摄入量密切相关,且增加干物质、有机质摄入量以及奶牛体重等预测因子对粪便N、P产生量的预测方程的精度具有显著的提高。

|
相比于国外,我国同类研究的相关文献较少。杨增玲等[20]以摄入日粮的氮、磷含量以及体重为自变量,建立了快速预测生长育肥猪粪便氮、磷含量的预测模型。李莉[35]、胡峥峥[36]等基于日粮氮、磷摄入量分别对蛋鸡、肉鸡粪便排出物中氮、磷含量进行了预测,预测模型详见表 5。研究结果均表明,畜禽粪便中氮、磷的含量与日粮中相应元素的摄入量呈正相关,即日粮中氮的摄入量越高,畜禽粪便中相应元素的排泄量也越高。但由于样本数较少,代表性较弱,相关预测方程的R2值较小,预测精度相对较低。

|
研究表明畜禽粪便的理化指标,如比重SG、电导率EC、干物质DM以及总固体TS等与其有机质、氮、磷含量等存在较强的相关关系[37-43],基于粪便理化指标可建立快速预测其有机质、氮、磷含量的回归方程。欧美许多研究人员如Dragun[21]、Martinez-Suller等[38]、Tunney[39]、Scotford等[40]、Marino等[41] 从肥料的角度出发,研究了利用粪便理化指标快速预测其有机质、氮、磷含量的可行性。我国部分研究人员如韩鲁佳等[24],李莉[35],胡峥峥[36],杨增玲[44]也建立了基于粪便理化指标预测肉鸡、蛋鸡及生长育肥猪粪便有机质、氮、磷含量的回归方程(表 6)。研究结果表明,粪便有机质含量与其比重SG[37]、干物质DM[41]具有较强的线性相关性,预测方程的相关系数可达0.9以上,表明基于粪便比重SG及干物质DM可精确地预测粪便有机质含量。而粪便总氮含量与总固体TS、干物质DM、比重SG及电导率EC等的一元线性相关性不强,但基于该自变量建立的二元或多元回归方程的相关系数较高,利用此回归方程可精确预测粪便总氮含量。粪便总磷与干物质DM、密度ρ、pH值及比重SG的线性相关性较强,基于其建立的回归方程的相关系数均在0.8以上。表明基于畜禽粪便理化指标干物质DM、密度ρ、pH值及比重SG可精确地预测粪便总磷含量。
|
近红外光谱分析(Near Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy,简称NIRS)是将光谱测量技术、计算机技术、化学计量学技术与基础测试技术有机结合的一种通过模型来识别、定量的间接分析技术。首先通过采集已知样品的近红外光谱图,并通过化学计量学对光谱进行处理,将其与不同性质参数的参考数据相关联,从而在光谱图和其参考数据之间建立起一一对映的映射关系,即模型。然后通过测定未知样品的光谱,并根据已建立的校正模型来快速预测未知样品的组成或性质[45]。
近红外光谱分析在快速测定畜禽粪便主要污染物含量方面的研究已经得到了重视,近几年国外一些研究机构对此方法的可行性进行了大量的研究工作[46-48]。Reeves等[49]利用近红外光谱分析技术对奶牛粪便的总碳、总氮和铵态氮的含量进行了测定,发现基于NIRS测定值建立的定标方程的相关系数均大于0.9,但对磷的预测精度较低。Saeys等[26] 考察了利用可见光和近红外反射光谱对猪粪有机质、总氮、氨氮以及磷、钾、钙、镁等营养物质含量进行在线分析的潜力。之后,Beccaccia等[50]和Wnetrzak[51]等利用近红外光谱分析对猪粪干物质、挥发性固体、有机质以及总氮等的预测精度进行了进一步验证。Tamburini等[52]也利用近红外光谱分析对家禽粪便中各形态的N(总氮、氨氮、有机氮、水溶性有机氮等)的含量进行了预测。研究结果均表明,近红外光谱分析可精确地预测粪便有机质、干物质及氮、磷含量。
国内研究人员从粪便肥料成分的角度出发,对不同畜种粪便主要污染物含量也做了相关的研究。崔兰英等[53]利用近红外反射光谱技术对奶牛粪便中的总氮、总磷以及铵态氮的含量进行了测定,建立的模型的判定系数均在0.95以上。樊霞等[54]也研究发现肉牛粪便中总氮、总磷、总钾及铵态氮的NIRS测定值均达到了与真实值相似的水平。此外,杨增玲[44]、孔源[55]相继利用近红外光谱分析技术快速预测了生长肥育猪及肉鸡粪便中主要污染物含量。进一步证明,近红外光谱分析技术可精确地预测畜禽粪便主要污染物含量。
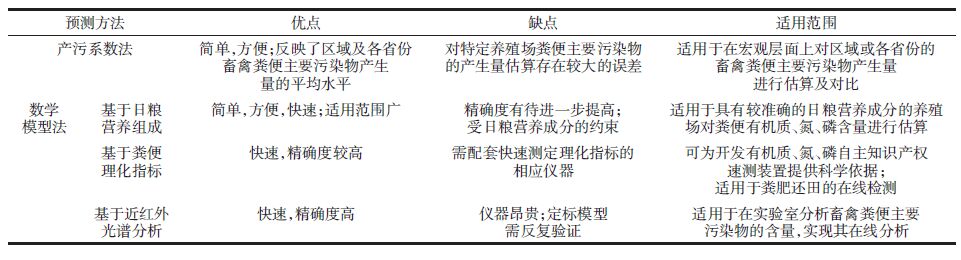
3 讨论综合分析2种预测方法,产污系数法在估算畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量时具有简单、快速的特点,在大区尺度上具有较高的预测精度。其中全国或大区产污系数反映了全国畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量的平均水平,适用于在宏观层面上对区域畜禽养殖粪便主要污染物产生量进行估算与预测,为宏观了解畜禽养殖业的产污状况、制定防治政策提供基础数据。而分省或分地区的产污系数则主要针对各省典型畜禽养殖的粪便特性,对其主要污染物的产生量进行估算。该类系数更符合各省畜禽养殖的特点,实用性更强,更能真实反映各省或各地区畜禽养殖主要污染物的产生量,可为各地区合理制定养殖业发展规划提供科学依据。但由于产污系数主要反映畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量的平均值,而对特定养殖场粪便污染物含量的估算精度相对较低。
数学模型法则主要基于畜禽粪便的特性对其主要污染物含量进行预测,其结果更加接近真实值,也具有更广泛的适用性。基于日粮营养组成预测畜禽粪便主要污染物含量时,不需要借助特定的仪器,即可由摄入的养分含量直接预测粪便主要污染物含量,对实际生产十分有利。尤其是较适合可获得日粮营养组成的规模化养殖场对其畜禽粪便有机质、氮、磷含量进行估算,为其粪便的资源化和无害化利用提供基础数据。同时该模型也可为规模化养殖场从日粮角度上寻求减排措施提供一定的参考。但由于动物代谢过程十分复杂,且建立模型的数据来源有限,该类预测模型的精度普遍不高。基于粪便理化指标建立的预测其有机质、氮、磷含量的回归方程精度较高,在实际应用中,该预测模型需配套相应理化指标如电导率EC、pH值等快速检测装置以实现粪便主要污染物含量的快速预测。该方法有助于相关技术人员研制开发粪便有机质、氮、磷自主知识产权速测装置,对于畜禽粪便的资源化利用特别是粪肥还田的在线检测具有重要指导意义。基于近红外光谱分析建立的模型预测精度较高,可快速、方便、简单、准确地分析多种组分,可替代畜禽粪便有机质、氮、磷等的传统测定方法,适用于在实验室分析畜禽粪便的有机质、氮、磷含量,实现畜禽粪便主要污染物含量的在线分析。但近红外光谱仪器昂贵,一次性投入大,对操作人员的专业知识要求较高,并且所建立的定标模型需要反复定标、验证和不断升级优化[41]。
各预测方法有其各自的优缺点和适用范围(表 7),在实际应用中,应根据研究目的,选择合适的预测方法,尽可能实现对畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量的精确预测。
|
通过对国内外畜禽粪便主要污染物产生量预测方法(即产污系数法与数学模型法)的主要特点及适用范围进行归纳与总结,认为产污系数法在大区尺度上具有较高的预测精度,适用于在宏观层面上对全国或各省份畜禽养殖粪便主要污染物产生量进行估算与预测,为宏观了解畜禽养殖业的产污状况、制定防治政策提供基础数据。数学模型法则主要基于各养殖场畜禽粪便的特性对其主要污染物含量进行预测,其结果更加接近真实值,也具有更广泛的适用性。其中基于日粮营养组成建立的预测模型精度相对较低,适用于可获得日粮营养组成的规模化养殖场对其畜禽粪便有机质、氮、磷含量进行估算,为其粪便的资源化和无害化利用提供基础数据。基于粪便理化指标建立的预测模型精度较高,有助于相关技术人员基于已建立的回归方程研制开发粪便有机质、氮、磷自主知识产权速测装置,对于实现粪肥还田的在线检测具有重要指导意义。基于近红外光谱分析建立的预测模型精度高,适用于在实验室分析畜禽粪便的有机质、氮、磷含量,实现畜禽粪便主要污染物含量的在线分析。
但目前我国对各预测方法的研究仍存在一些问题和不足,需要进一步改进和完善。
(1)产污系数目前的地理大区分类方法并不能完全区分各地区气候条件,而且在测算时间的选择上,虽然各研究均采用每个季节分别采样的方式来规避季节因素的影响,但采样时段的选择并不统一,甚至差别很大。因此,需进一步规范产污系数的测算操作,提高其测算方法的适用性和准确性。
(2)我国在计算畜禽养殖业产污系数时,并未分别给出畜禽粪便与尿液各污染物的产生系数。而在实际应用中,有时更需要了解畜禽粪便与尿液各自的产污系数。因此,有待进一步完善畜禽产污系数手册,对粪便和尿液的产污系数分别进行核算。
(3)由于不同畜种各生长阶段养殖量的统计数据较难获得,利用《第一次全国污染源普查畜禽养殖业产排污系数手册》精确估算全国畜禽养殖粪便主要污染物产生量具有一定难度。因此如何将产污系数与统计数据相对应,扩大产污系数的适用范围,提高其估算精度是进一步完善产污系数手册需考虑的问题。
(4)随着畜禽养殖模式、饲料组成等不断变化,产污系数需不断更新以适应规模化的畜禽养殖模式。
(5)基于日粮营养组成建立的预测模型的精确度相对较低,造成这种现象的原因一方面与动物自身复杂的代谢机理有关,另一方面主要是由于建立模型的基础数据有限,数据的代表性和普遍性不高。因此应开展以大数据为基础的模型建立,提高模型的精确度并进一步扩大模型的适用范围。
(6)目前我国基于理化指标和近红外光谱分析建立的预测粪便主要污染物含量的模型研究相对普遍,且精度相对较高,但仍集中于理论研究阶段,缺乏对各预测方法的实际应用。因此亟需基于已建立的回归方程研制开发在线检测装置和方法,实现畜禽粪便主要污染物含量的在线检测。
| [1] | 农文协. 畜产环境对策大事典[M]. 东京: 东京农山渔村文化协会出版社 ,1995 . The Association of Agricultural Livestock. Counter measures chronicle[M]. Tokyo: Tokyo Nousangyoson Culture Association Press , 1995 . (in Chinese) |
| [2] | Poulsen H D, Kristensen V F. Standard values for farm manure: A reval-uation of the Danish standard values concerning the nitrogen, phospho-rus and potassium content of manure[M]. Denmark: Danish Institute of Agricultural Sciences , 1998 . |
| [3] | American Society of Agricultural Engineers. Manure production and characteristics[S]. America: American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 2005. |
| [4] | 国家环境保护部自然生态保护司. 全国规模化畜禽养殖业污染情况调查及防治对策[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社 ,2002 : 77 -78. Department of Nature and Ecology Conservation, State Environmental Protection Administration. Investigation and control measures of pollu-tion in the scale of livestock and poultry breeding industry in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press , 2002 : 77 -78. (in Chinese) |
| [5] | 中国农业科学院农业环境与可持续发展研究所,环境保护部南京环境科学研究所. 第一次全国污染源普查畜禽养殖业产排污系数手册[EB/OL]. http://doc.mbalib.com/view/e46ba36add1542acdfaa10bf7db6c5a.html(2009-02). Institute of Environment and Sustainable Development in Agriculture, CAAS, Nanjing Institute of Environmental Sciences, MEP. A manual of the first national census of pollutant generation and discharge coefficient of livestock and poultry breeding industry[EB/OL]. http://doc.mbalib.com/view/e4c6ba36add1542acdfaa10bf7db6c5a.html(2009-02). (in Chinese) |
| [6] | 董红敏, 朱志平, 黄宏坤, 等. 畜禽养殖业产污系数和排污系数计算方法[J]. 农业工程学报 , 2011, 27 (1) : 303–308. DONG Hong-min, ZHU Zhi-ping, HUANG Hong-kun, et al. Pollutant generation coefficient and discharge coefficient in animal production[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering , 2011, 27 (1) : 303–308. (in Chinese) |
| [7] | 苏文幸. 生猪养殖业主要污染源产排污量核算体系研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学,2012. SU Wen-xing. Study on accounting system of the amount of pollutants producing and pollutants discharge in the main pollution sources of live pig farming industry[D]. Changsha:Hunan Normal University, 2012. (in Chinese) |
| [8] | 谢飞, 曹磊, 王震, 等. 江苏省太湖地区畜禽业产排污测算[J]. 水土保持通报 , 2014, 34 (2) : 128–133. XIE Fei, CAO Lei, WANG Zhen, et al. Estimation of pollutant produc-tion and discharge from livestock and poultry industries in Taihu Lake region[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation , 2014, 34 (2) : 128–133. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | 汪开英, 刘健, 陈小霞, 等. 浙江省畜禽业产排污测算与土地承载力分析[J]. 应用生态学报 , 2009, 20 (12) : 3043–3048. WANG Kai-ying, LIU Jian, CHEN Xiao-xia, et al. Pollutant production and discharge from livestock and poultry industries and land carrying capacity in Zhejiang Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecol-ogy , 2009, 20 (12) : 3043–3048. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | 何志平, 曾凯, 李正确, 等. 四川规模猪场产排污系数测定[J]. 中国沼气 , 2010, 28 (4) : 10–14. HE Zhi-ping, ZENG Kai, LI Zheng-que, et al. Measurement of pollu-tants producing and discharging coefficient on large scale pig farms in Sichuan[J]. China Biogas , 2010, 28 (4) : 10–14. (in Chinese) |
| [11] | 王会群, 高腾云, 史鹏飞, 等. 奶牛集约化生产体系中氮素产污系数的测定[J]. 江苏农业科学 , 2010 (3) : 444–446. WANG Hui-qun, GAO Teng-yun, SHI Peng-fei, et al. Determination of nitrogen pollution coefficients in intensive production system of dairy[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences , 2010 (3) : 444–446. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | 栾冬梅, 李士平, 马君, 等. 规模化奶牛场育成牛和泌乳牛产排污系数的测算[J]. 农业工程学报 , 2012, 28 (16) : 185–189. LUAN Dong-mei, LI Shi-ping, MA Jun, et al. Calculation of pollutants producing and discharging coefficients of heifers and lactating dairy cows in large-scale dairy farms[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering , 2012, 28 (16) : 185–189. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | 张振伟, 庞伟英, 周玉香, 等. 宁夏地区不同生长阶段奶牛产污系数的对比分析[J]. 家畜生态学报 , 2015, 36 (1) : 50–54. ZHANG Zhen-wei, PANG Wei-ying, ZHOU Yu-xiang, et al. Compar-ative analysis on pollutant producing coefficients of lactating cows at different growth stages in Ningxia[J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecol-ogy , 2015, 36 (1) : 50–54. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | 周天墨, 付强, 诸云强, 等. 中国分省畜禽产污系数优化及污染物构成时空特征分析[J]. 地理研究 , 2014, 33 (4) : 762–776. ZHOU Tian-mo, FU Qiang, ZHU Yun-qiang, et al. Optimizing pollu-tant generation coefficients of livestock industry and mapping patterns of the pollutant constitution in China[J]. Geographical Research , 2014, 33 (4) : 762–776. (in Chinese) |
| [15] | 林源, 马骥, 秦富. 中国畜禽粪便资源结构分布及发展展望[J]. 中国农学通报 , 2012, 28 (32) : 1–5. LIN Yuan, MA Ji, QIN Fu. The structure distribution and prospect of china manure resource[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin , 2012, 28 (32) : 1–5. (in Chinese) |
| [16] | 耿维, 胡林, 崔建宇, 等. 中国区域畜禽粪便能源潜力及总量控制研究[J]. 农业工程学报 , 2013, 29 (1) : 171–179. GENG Wei, HU Lin, CUI Jian-yu, et al. Biogas energy potential for livestock manure and gross control of animal feeding in region level of China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering , 2013, 29 (1) : 171–179. (in Chinese) |
| [17] | Tomlinson A P, Powers W J, Van Horn H H, et al. Dietary protein effects on nitrogen excretion and manure characteristics of lactating cows[J]. Transactions of The ASAE , 1996, 39 (4) : 1441–1448. DOI:10.13031/2013.27637 |
| [18] | Nennich T D, Harrison J H, Van Wieringen L M, et al. Prediction of manure and nutrient excretion from dairy cattle[J]. Journal of Dairy Science , 2005, 88 (10) : 3721–3733. DOI:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)73058-7 |
| [19] | Higgs R J, Chase L E, Van Amburgh M E. Development and evaluation of equations in the Cornell net carbohydrate and protein system to predict nitrogen excretion in lactating dairy cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science , 2012, 95 (4) : 2004–2014. DOI:10.3168/jds.2011-4810 |
| [20] | 杨增玲, 韩鲁佳, 刘依, 等. 基于摄入养分含量预测猪新鲜粪便肥料成分含量的试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报 , 2004, 20 (1) : 278–283. YANG Zeng-ling, HAN Lu-jia, LIU Yi, et al. Experimental study on estimating fertilizer value of raw swine slurries based on nutrients in-take[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineer-ing , 2004, 20 (1) : 278–283. (in Chinese) |
| [21] | Dragun W. Quantitative and qualitative characteristics of manure from closed cycle pig farms[C]. Proceedings of The Rural Design Official Association, Szczecin, Poland: 1978. |
| [22] | Moral R, Perez-Murcia M D, Perez-Espinosa A, et al. Estimation of nutrient values of pig slurries in southeast Spain using easily determined properties[J]. Waste Management , 2005, 25 (7) : 719–725. DOI:10.1016/j.wasman.2004.09.010 |
| [23] | Suresh A, Choi H L, Oh D I, et al. Prediction of the nutrients value and biochemical characteristics of swine slurry by measurement of EC-Electrical conductivity[J]. Bioresource Technology , 2009, 100 (20) : 4683–4689. DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.05.006 |
| [24] | 韩鲁佳, 胡峥峥, 阎巧娟, 等. 肉鸡粪便理化指标与其肥料成分含量的相关关系研究[J]. 农业工程学报 , 2002, 18 (6) : 123–126. HAN Lu-jia, HU Zheng-zheng, YAN Qiao-juan, et al. Correlations between chemical-physical properties and nutrient contents in broiler manure[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engi-neering , 2002, 18 (6) : 123–126. (in Chinese) |
| [25] | Reeves J B. Near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for the analysis of poultry manures[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chem-istry , 2001, 49 (5) : 2193–2197. DOI:10.1021/jf0013961 |
| [26] | Saeys W, Mouazen A M, Ramon H. Potential for onsite and online analysis of pig manure using visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Biosystems Engineering , 2005, 91 (4) : 393–402. DOI:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.05.001 |
| [27] | 娜仁花, 董红敏. 日粮类型对奶牛粪尿特性及氮排放的影响[J]. 畜牧与兽医 , 2012, 44 (5) : 26–30. NA Ren-hua, DONG Hong-min. Effects of dietary categories on feces/urine features and nitrogen emission in dairy cows[J]. Animal Hus-bandry & Veterinary Medicine , 2012, 44 (5) : 26–30. (in Chinese) |
| [28] | 娜仁花, 王月, 刘思强, 等. 日粮类型对奶牛产污的影响[J]. 中国饲料 , 2014 (3) : 22–25. NA Ren-hua, WANG Yue, LIU Si-qiang, et al. Effects of diets on pol-lutants produced by dairy cows[J]. China Feed , 2014 (3) : 22–25. (in Chinese) |
| [29] | 何余湧, 罗建华, 吴志勇, 等. 饲料对生猪养殖小区粪便产量及粪便污染物背景值的影响[J]. 饲料工业 , 2010, 31 (15) : 51–54. HE Yu-yong, LUO Jian-hua, WU Zhi-yong, et al. Effect of feed on amount of fecal and background value of contaminants fecal in pig breeding[J]. Feed Industry , 2010, 31 (15) : 51–54. (in Chinese) |
| [30] | 冯春霞. 合理调制饲料, 降低家禽粪便对环境的污染[J]. 中国禽业导刊 , 2008, 24 (22) : 37. FENG Chun-xia. Reduce pollution of poultry manure on environment by concocting the feed reasonably[J]. Guide to Chinese Poultry , 2008, 24 (22) : 37. (in Chinese) |
| [31] | Yan T, Frost J P, Agnew R E, et al. Relationships among manure nitro-gen output and dietary and animal factors in lactating dairy cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science , 2006, 89 (10) : 3981–3991. DOI:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72441-9 |
| [32] | Jiao H P, Yan T, McDowell D A. Prediction of manure nitrogen and or-ganic matter excretion for young Holstein cattle fed on grass silage-based diets[J]. Journal of Animal Science , 2014, 92 (7) : 3042–3052. DOI:10.2527/jas.2013-7552 |
| [33] | Prapaspongsa T, Poulsen H D, Jørgensen H. Prediction of manure ni-trogen and carbon output from grower-finisher pigs[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology , 2009, 151 (1) : 97–110. |
| [34] | Jørgensen H, Prapaspongsa T, Poulsen H D. Models to quantify excre-tion of dry matter, nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon in growing pigs fed regional diets[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology , 2013, 4 (1) : 1–9. DOI:10.1186/2049-1891-4-1 |
| [35] | 李莉. 预测蛋鸡粪便肥料成分含量的试验研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2003. LI Li. Study on quick estimating of the nutrient contents in layer ma-nure[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2003.(in Chinese) |
| [36] | 胡峥峥. 预测家禽粪便肥料成分含量的试验研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2001. HU Zheng-zheng. Estimation of the nutrient contents in poultry ma-nure[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2001.(in Chinese) |
| [37] | Yang Z, Han L, Li Q, et al. Estimating nutrient contents of pig slurries rapidly by measurement of physical and chemical properties[J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science , 2006, 144 (3) : 261–267. DOI:10.1017/S0021859606006095 |
| [38] | Martinez-Suller L, Azzellino A, Provolo G. Analysis of livestock slur-ries from farms across northern Italy: Relationship between indicators and nutrient content[J]. Biosystems Engineering , 2008, 99 (4) : 540–552. DOI:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2007.12.002 |
| [39] | Tunney H. Dry matter, specific gravity and nutrient relationships of cattle and pig slurry[C]//Hawkins J C: Engineering problems with efflu-ents from livestock, the directorate general for agriculture, coordination of agricultural Research, 1979: 430-444. |
| [40] | Scotford I M, Cumby T R, White R P, et al. Estimation of the nutrient value of agricultural slurries by measurement of physical and chemical properties[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research , 1998, 71 (3) : 291–305. DOI:10.1006/jaer.1998.0326 |
| [41] | Marino P, De Ferrari G, Bechini L. Description of a sample of liquid dairy manures and relationships between analytical variables[J]. Biosystems Engineering , 2008, 100 (2) : 256–265. DOI:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2008.02.012 |
| [42] | 崔兰英, 杨增玲, 韩鲁佳, 等. 基于理化指标快速预测奶牛粪便肥料成分含量[J]. 中国农业大学学报 , 2006, 11 (2) : 98–102. CUI Lan-ying, YANG Zeng-ling, HAN Lu-jia, et al. Rapidly estimat-ing fertilizer value of dairy manure based on physical and chemical properties[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University , 2006, 11 (2) : 98–102. (in Chinese) |
| [43] | Huang G, Wang X, Han L. Rapid estimation of nutrients in chicken manure during plant-field composting using physicochemical proper-ties[J]. Bioresource Technology , 2011, 102 (2) : 1455–1461. DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.086 |
| [44] | 杨增玲. 生长肥育猪粪便主要成分含量快速预测方法和模型的研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2005. YANG Zeng-ling. Rapid prediction methods and models of the nutrient contents of fattening pig manure[D]. Beijing:China Agricultural Uni-versity, 2005.(in Chinese) |
| [45] | 张卉, 宋妍, 冷静, 等. 近红外光谱分析技术[J]. 光谱实验室 , 2007, 24 (3) : 388–395. ZHANG Hui, SONG Yan, LENG Jing, et al. Near infrared spectroscopy analysis technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory , 2007, 24 (3) : 388–395. (in Chinese) |
| [46] | Reeves J B. The present status of "quick tests"for on-farm analysis with emphasis on manures and soil: What is available and what is lack-ing?[J]. Livestock Science , 2007, 112 (3) : 224–231. DOI:10.1016/j.livsci.2007.09.009 |
| [47] | Malley D F, Yesmin L, Eilers R G. Rapid analysis of hog manure and manure-amended soils using near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Soil Sci-ence Society of America Journal , 2002, 66 (5) : 1677–1686. DOI:10.2136/sssaj2002.1677 |
| [48] | Ye W, Lorimor J C, Hurburgh Jr C R, et al. The transfer of beef cattle feedlot manure calibrations between near-infrared spectrophotometers using three standardization techniques[C]. The Ninth International Animal, Agricultural and Food Processing Wastes Proceedings, North Carolina, USA, ASAE, 2003: 637-646. |
| [49] | Reeves J B, Van Kessel J S. Near-infrared spectroscopic determination of carbon, total nitrogen, and ammonium-N in dairy manures[J]. Jour-nal of Dairy Science , 2000, 83 (8) : 1829–1836. DOI:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(00)75053-3 |
| [50] | Becaccia A, Ferrer P, Ibañez M A, et al. Relationships among slurry characteristics and gaseous emissions at different types of commercial Spanish pig farms[J]. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research , 2015, 13 (1) : 1–15. |
| [51] | Wnetrzak R, Hayes D J M, Jensen L S, et al. Determination of the high-er heating value of pig manure[J]. Waste and Biomass Valorization , 2015, 6 (3) : 327–333. DOI:10.1007/s12649-015-9350-y |
| [52] | Tamburini E, Castaldelli G, Ferrari G, et al. Onsite and online FT-NIR spectroscopy for the estimation of total nitrogen and moisture content in poultry manure[J]. Environmental Technology , 2015, 36 (18) : 1–20. |
| [53] | 崔兰英, 杨增玲, 韩鲁佳, 等. 近红外技术快速测定奶牛粪便主要肥料成分含量的研究[C]. 农业工程科技创新与建设现代农业——2005年中国农业工程学会学术年会论文集第五分册, 2005: 242-245. CUI Lan-ying, YANG Zeng-ling, HAN Lu-jia, et al. Study on rapid prediction of the nutrients contents of dairy manure by NIRS[C]. A-gricultural engineering science and technology innovation and the con-struction of modern agriculture-The Fifth Annual Conference Volume of Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering Proceedings, 2005: 242-245.(in Chinese) |
| [54] | 樊霞, 韩鲁佳, 皇才进, 等. 基于近红外光谱技术的牛粪成分含量测定方法[J]. 农业机械学报 , 2006, 37 (3) : 76–79. FAN Xia, HAN Lu-jia, HUANG Cai-jin, et al. Determination of nutri-ent contents in beef manure with near infrared reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery , 2006, 37 (3) : 76–79. (in Chinese) |
| [55] | KONG Yuan. Study on quick prediction methods of nutrient contents in broiler manure[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2005.(in Chinese) |
 2016, Vol. 33
2016, Vol. 33