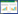文章信息
- 杨景娜, 黄青青, 范荣霞, 李花粉, 罗新湖, 宋萍, 乔玉辉
- YANG Jing-na, HUANG Qing-qing, FAN Rong-xia, LI Hua-fen, LUO Xin-hu, SONG Ping, QIAO Yu-hui
- 新疆伊犁州农用土壤中Cu和Zn的含量分布
- Analysis on Cu and Zn Concentrations in Agricultural Soils of Ili District, Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China
- 农业资源与环境学报, 2015, 32(1): 8-13
- Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(6): 513-520
- http://dx.doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2014.0231
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2014-09-17
2. 新疆伊犁州农业技术推广总站, 新疆伊宁835000
2. Ili Agro-Tech Extension and Service Center, Yining 835000, China
土壤环境质量的优劣直接影响着人类的生产、生 活和发展,然而工业化和农业现代化的迅速发展,使 越来越多的污染物累积到土壤环境中,农田土壤中重 金属的累积已经引起越来越多的公众关注[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]。重金属 可以通过多种途径进入土壤,工业产生的三废,可通 过大气沉降、污灌、污泥农用途径进入土壤[2, 6, 7, 8, 9];农业 生产中化肥、有机肥和农药的不合理施用,可不同程 度污染农田生态系统[10, 11]。重金属在土壤中的累积可 以通过食物链在生物体内富集,最终可能危害人体健 康[12]。Cu 和Zn 虽然是植物和人体必需的营养元素,但是超过一定的限值也会对植物和人体产生危害[13]。 Cu和Zn 作为饲料添加剂在饲料生产中的广泛使用, 使有机肥料中的Cu、Zn 含量明显增加,并随着肥料 的施入在农田中积累[11, 14]。Cu 和Zn 很容易在土壤中 累积并在农产品中富集,通过食物链在动物及人体内 富集,影响人体健康。
伊犁州作为新疆乃至西部重要的生态农林牧资 源基地,是发展生态产业基地的最佳区域之一。然而 作为绿色食品和有机食品的生产基地,其产地环境条 件必须符合标准的要求,因此对该地区的环境评价是 必不可少的,而土壤环境是评价的重要环节之一。本 研究对新疆伊犁州的农用土壤重金属含量进行了取 样分析,并进行了质量评价,研究结果有助于了解伊 犁州土壤中Cu 和Zn 的含量水平,为该地区绿色食 品和有机食品的基地建设提供指导。 1 材料与方法 1.1 研究区概况
伊犁哈萨克自治州位于祖国西北边陲,新疆西 部,三山环抱。伊犁河谷年有效积温达3 170~4 100 益,日照可达2 820 h,地理坐标为东经81°26′~81°37′, 北纬43°49′~43°53′。据全国第二次土壤普查结果伊 犁河谷土壤类型主要有:潮土、灌耕土、草甸土、沼泽 土、黑钙土、灌耕黑钙土、栗钙土等,且土壤呈现“两 高”“一厚”“微碱性”的特点,“两高”指有机质含量高、 速效钾含量高;“一厚”指土层厚,一般>1 m;“微碱性” 指土壤pH值中偏微碱,范围为7.3~8.4之间。 1.2 样品采集与分析
考虑地形地貌、土壤类型、植被类型及空间均匀 性与代表性等因素,依据绿色食品产地环境技术条件 (NY/T 391—2013)中的相关规定,对伊犁州耕地土壤 进行了布点采样。在全州8 个县共设置采样点600 个,较均匀地分布于各县所辖乡镇的自然村,平均每 个村采样1~2 个,各乡平均10~20 个样,样点分布图 见图 1。采样选择有代表性的田块,5~10 点混合,采样 深度为0~20 cm表土层。
|
| 图 1 新疆伊犁州农用土壤采样点分布示意图 Figure 1 Distribution of the sampling sites in Ili District,Xinjiang |
土壤样品自然风干,剔除样品中植物根系,用木 棍碾碎,先过60 目筛,之后样品通过四分法分取其中 一部分,用研钵研磨过100 目尼龙网筛,样品存放于 自封袋中待测,整个过程避免与含重金属元素的物品 接触。样品通过王水(HCl:HNO3=3:1)浸泡过夜,之 后微波消解(美国CEM 公司,MARS5)。消解液用火 焰-原子吸收分光光度计(TAS-990)进行浓度测定, 测定方法Cu、Zn 的检出限分别为0.006 mg·L-1 和 0.002 mg·L-1。样品消解过程中使用的各种酸均为优 级纯,分析过程加入空白及国家土壤标准样品GSBZ 50011-88(ESS-1)进行分析质量控制,分析过程中Cu 和Zn 回收率分别达到95%~110%和90%~118%。 1.3 数据处理与评价标准
测定数据用Excel 进行分析,采用Sigmaplot 软 件进行图表的制作,同时为了进一步对重金属含量、 重金属空间结构特征进行分析,采用重金属半方差函 数模型和普通克里格插值法,借助ArcGIS9.2 软件绘 制土壤中Cu 和Zn 含量的克里格插值图。
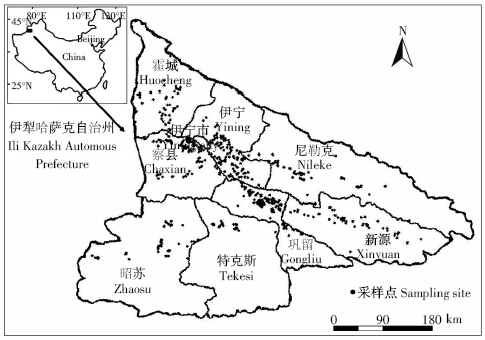
本研究的目的是评价新疆伊犁州的土壤环境是 否符合我国绿色食品和有机食品对产地环境的要求, 因此本文采用2013 年农业部颁布的“绿色食品产地 环境技术条件”(NY/T 391—2013)以及2011 年国家 质量监督检验检疫总局和国家标准化管理委员会颁 布的“中国有机产品标准”(GB/T 19630—2011)中的 要求进行评价。按照中国有机产品标准的要求,有机 产品的产地环境质量应符合国家环境保护总局1995 年颁布的“土壤环境质量标准”(GB 15618—1995)中 的二级标准。绿色食品和有机食品的产地土壤环境评 价标准见表 1。由于伊犁州土壤pH值中偏微碱,范围 为7.3~8.4 之间,因此评价时参考pH 6.5~7.5 规定的 限值。
 |
2.1 伊犁州土壤Cu 和Zn含量统计
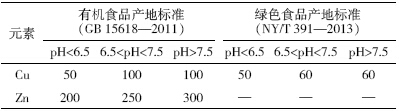
伊犁州土壤Cu 和Zn 含量统计分析见表 2。由表 2 可以看出,新疆伊犁州土壤中的Cu、Zn 含量范围分 别为11.07~59.90 mg·kg-1和39.58~160.40 mg·kg-1,平 均值分别为28.68 mg·kg-1和83.17 mg·kg-1。与表 1 中的评价标准相比,所有采样点的Cu 和Zn含量均符合 我国有机食品和绿色食品对产地环境的要求。由于新 疆伊犁河谷重工业企业较少,基本上没有大的污染 源,空气质量、水质质量均符合国家相应的质量标准, 农药、化肥的使用量也低于全国标准[15]。因此土壤采 样的分析结果也表明该地区土壤中Cu 和Zn 含量均 没有超过标准规定的限值。
 |
但是与我们国家20 世纪80 年代新疆土壤Cu、 Zn 元素背景值相比较[16],土壤中的Cu、Zn 的平均含 量均有所增加,分别增加了7%和21%。变异系数是 反映样品变异程度的一个统计量,能在一定程度上反 映样品受人为影响的程度,从变异系数来看(表 2)Cu 元素的变异系数比Zn高,达到30.07%,Zn为19.71%。 以上分析表明,在人为活动的影响下,伊犁州土壤中 Cu和Zn 已经存在一定程度的累积,但是污染风险相 对较小。
伊犁州全州土壤中Cu、Zn 含量的频数分布图见 图 2。全州土壤Cu、Zn 含量Sigmaplot 盒状图见图 3。 由图 2 及图 3 可以看出,新疆伊犁州土壤中的Cu、Zn 含量盒状图与频数分布图呈现出相同的规律。土壤中 Cu 的含量约有85%的数据分布在20~40 mg·kg-1 之 间;同时土壤中的Zn 含量有90%分布在60~110 mg· kg-1之间。
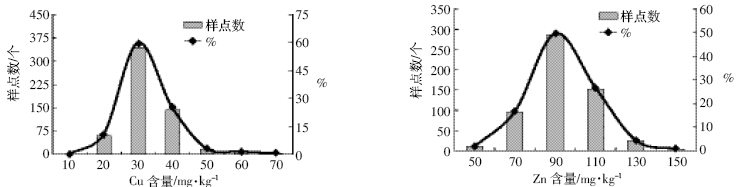
|
| 图 2 伊犁州土壤Cu、Zn 含量统计 Figure 2 Statistics of Cu and Zn contents in the agricultural soils of Ili District |
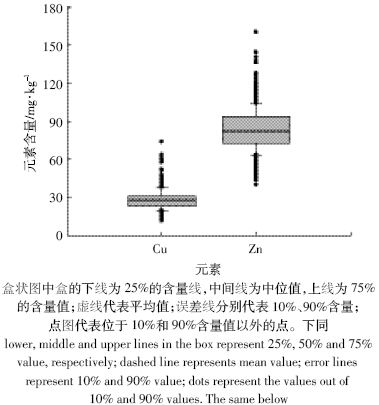
|
| 图 3 伊犁州土壤Cu、Zn 含量分布 Figure 3 Distribution of Cu and Zn contents in the agricultural soils of Ili District |
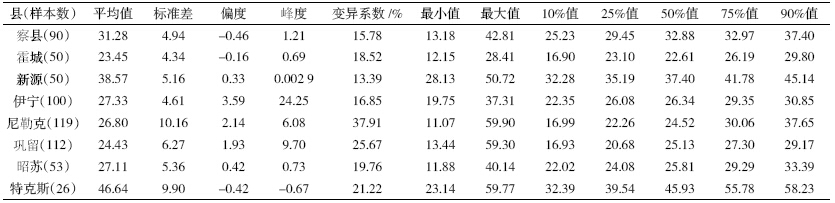
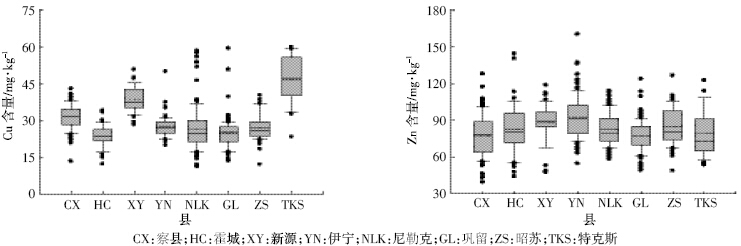
伊犁州8 个县土壤中Cu、Zn 含量统计分析见表 3 和表 4。伊犁州8 个县的自然环境包括海拔、气候、 植被等都有各自的特点,土壤的性质受各种因素的影响也有所差异,土壤中的重金属元素的含量分布也有 所不同。8 个县中特克斯县土壤中Cu 的平均含量最 高,霍城县最低,最大值出现在尼勒克县。而Zn 的平 均含量伊宁县最高,察县最低。从各个县的检测分析结果来看,伊犁州8 个县土壤中Cu 和Zn 的含量均 没有超过绿色食品和有机食品产地规定的限值。
 |
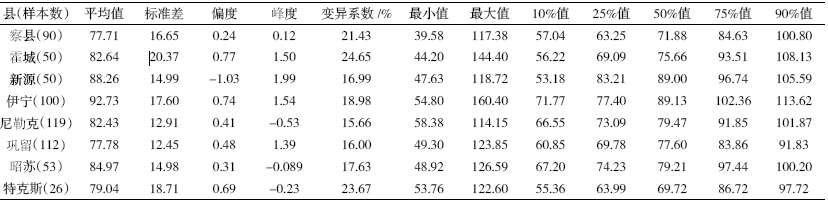 |
然而,各个县中Cu 和Zn 平均含量与新疆土壤 Cu 和Zn 元素背景值相比较各不相同(表 3 和表 4)。 其中霍城和巩留土壤中Cu 的平均含量低于背景值, 其余各县均高于背景值,特克斯县土壤中Cu 的平均 含量比背景值高75%;而8 个县中Zn 的平均含量均 高于背景值,伊宁县土壤中Zn 的平均含量比背景值 高33%。由于该地区的灌溉用水和空气质量较好,因 此土壤中Cu和Zn的累积主要是由于农用物质,例如 化肥和有机肥的施用[6, 17]以及含铜制剂的使用[6, 14, 18]。
虽然各县中土壤Cu 和Zn 含量均符合产地环境 要求,但是大多高于背景值,表明Cu 和Zn 在土壤中 产生了累积。
伊犁州8 个县土壤Cu、Zn 含量Sigmaplot 盒状图 见图 4。从图 4 可以看出,伊犁州8个县土壤中Cu 的 含量特克斯县较其他7 个县偏高,其次是新源县;8 个县土壤中Zn含量差异不大。
|
| 图 4 伊犁州8 个县土壤Cu、Zn 含量分布情况 Figure 4 Distribution of Cu and Zn contents in the agricultural soils of eight counties |
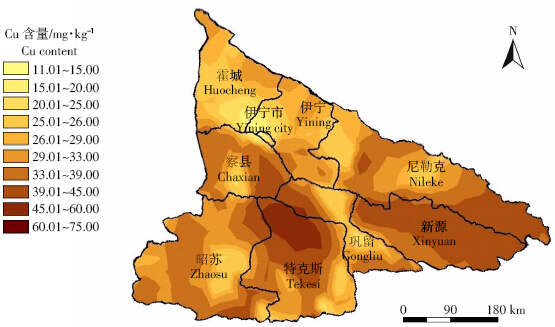
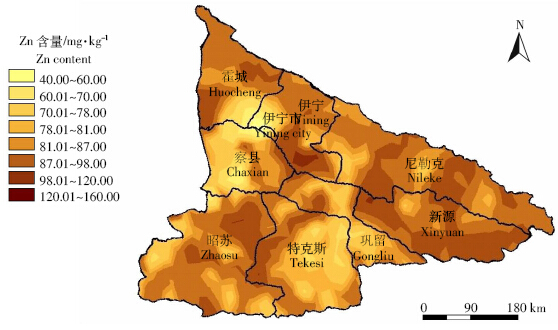
克里格插值是对离散变量进行连续无偏插值的 可靠方法,插值结果可以直观地呈现出重金属元素的 空间分布特征[19]。根据重金属元素分布形态,利用Arc- GIS9.2 软件中的地统计模块对Cu、Zn 2种元素进行普通克里格插值,最后得到伊犁州土壤中Cu、Zn 含 量的空间分布图见图 5和图 6。从图中可以看出伊犁州土壤中的Cu、Zn 含量在各县的差异较大,Cu 含量 较高的2 个县为特克斯与新源县;Zn 在全州的分布差异不大,这与以上分析结果一致。
|
| 图 5 伊犁州土壤Cu 含量空间分布情况 Figure 5 Spatial distribution of Cu content in the agricultural soils of Ili District |
|
| 图 6 伊犁州土壤Zn 含量空间分布情况 Figure 6 Spatial distribution of Zn content in the agricultural soils of Ili District |
(1)新疆伊犁州8 个县的农用土壤中Cu、Zn含量 均符合绿色食品产地环境技术条件以及中国有机产 品的产地环境质量要求。所有采样点土壤中Cu、Zn 含量均没有发现超标现象,该地区土壤中的Cu、Zn 含量环境污染风险不大。
(2)虽然土壤中Cu、Zn 含量没有发现超标现象, 但是与该地区20 世纪80年代的土壤背景值相比,有 上升的趋势,Cu 和Zn 的算术均值分别升高了7%和 21%。
| [1] | 岳子明, 李晓秀, 高晓晶. 北京通州区土壤环境质量模糊综合评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(4): 1402-1405. YUE Zi-ming, LI Xiao-xiu, GAO Xiao-jing. Fuzzy comprehensive as-sessment on soil environment of Tongzhou in Beijing[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007, 26(4): 1402-1405.(in Chinese) |
| [2] | Chen T B, Zheng Y M, Lei M, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 60(4): 542-551. |
| [3] | Abrahams P W. Soils: their implications to human health[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2002, 291(1-3): 1-32. |
| [4] | 贾琳, 杨林生, 欧阳竹, 等. 典型农业区农田土壤重金属潜在生态 风险评价[J].农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(11): 2270-2276. JIA Lin, YANG Lin-sheng, OUYANG Zhu, et al. Assessment of the po-tential ecological risk of heavy metals in the farmland soils in Yucheng City, Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(11): 2270-2276.(in Chinese) |
| [5] | MicóC, RecataláL, Peris M, et al. Assessing heavy metal sources in a-gricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 65(5): 863-872. |
| [6] | Nicholson F A, Smith S R, Alloway B J, et al. An inventory of heavy met-als inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2003, 311(1-3): 205-219. |
| [7] | Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L. Multivariate statistical and GISbased approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils[J]. Environmen-tal Pollution, 2001, 114(3): 313-324. |
| [8] | 姜勇,梁文举,张玉革, 等.污灌对土壤重金属环境容量及水稻生 长的影响研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2004, 12(3): 124-127. JIANGYong,LIANGWen-ju, ZHANGYu-ge, et al. Influence of wastew-ater irrigation on environmental capacity of soil heavy metals and rice growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2004, 12(3): 124-127. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | 孟凡祥, 李琪, 闻大中. 金属加工厂附近农田土壤锌污染的地统 计学分析[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 21(4): 367-370. MENG Fan-xiang, LI Qi, WEN Da-zhong, et al. Geostatistical analysis of soil zinc contamination in the vicinity of a metal-processing manu-facturer[J]. Journal of Shenyang Architectural and Civil Engineering In-stitute, 2005, 21(4): 367-370.(in Chinese) |
| [10] | Huang S S, Liao Q L, Hua M, et al. Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong district, Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 67(11): 2148-2155. |
| [11] | 姜萍,金盛杨, 郝秀珍,等.重金属在猪饲料-粪便-土壤-蔬菜中 的分布特征研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(5): 942-947. JIANG Ping, JIN Sheng-yang, HAO Xiu-zhen, et al. Distribution char-acteristics of heavy metals in feeds, pig manures, soils and vegetables[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(5): 942-947.(in Chinese) |
| [12] | Mclaughlin M J, Parker D R, Clarke J M. Metals and micronutrientsfood safety issues[J]. Field Crops Research, 1999, 60(1-2): 143-163. |
| [13] | Taylor M P, Mackay A K, Hudson-Edwards K A, et al. Soil Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn contaminants around Mount Isa city, Queensland, Australia: Po-tential sources and risks to human health [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2010, 25(6): 841-855. |
| [14] | 刘荣乐,李书田,王秀斌,等.我国商品有机肥料和有机废弃物中重 金属的含量状况与分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2005, 24(2): 392-397. LIU Rong-le, LI Shu-tian, WANG Xiu-bin, et al. Contents of heavy metals in commercial organic fertilizers and organic wastes[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2005, 24(2): 392-397.(in Chinese) |
| [15] | 孟凡乔,叶晨,焦子伟,等.伊犁地区绿色食品和有机农产品生产 现状、问题辨识与对策分析[J].新疆农业科学, 2008, 45(S3): 83-88. MENG Fan-qiao, YE Chen, JIAO Zi-wei, et al. The current production status, problem recognition and countermeasure analysis for green food and agricultural products of Ili District[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sci-ences, 2008, 45(S3): 83-88.(in Chinese) |
| [16] | 中国环境监测总站.中国土壤元素背景值[M].北京:中国环境科学 出版社, 1990. China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Soil background con-tents of elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990.(in Chinese) |
| [17] | 李双异,刘赫,汪景宽.长期定位施肥对棕壤重金属全量及其有 效性影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(6): 1125-1129. LI Shuang-yi, LIU He, WANG Jing-kuan. Effects of long-term located fertilization on heavy metals and their availability in brown earth[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(6): 1125-1129.(in Chinese) |
| [18] | Chen T B, Wong J W C, Zhou HY, et al. Assessment of trace metal dis-tribution and contamination in surface soils of Hong Kong[J]. Environ-mental Pollution, 1997, 96(1): 61-68. |
| [19] | 汤国安. 地理信息系统空间分析实验教程[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. TANG Guo-an. GIS spatial analysis experiments tutorial[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012.(in Chinese) |
 2015, Vol. 32
2015, Vol. 32